Figure 1.
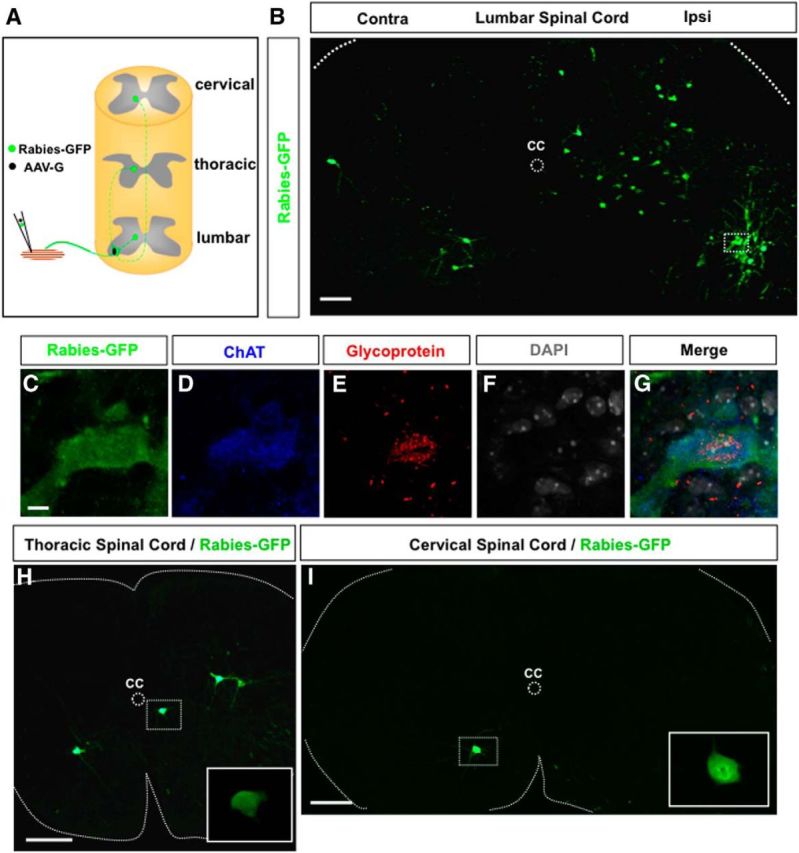
Trans-synaptic labeling of long descending premotor PPNs at the cervical and thoracic spinal levels. A, A schematic diagram of the experimental paradigm. A mixture of Rabies-GFP and AAV-G is injected into the hindlimb muscle TA of a P3 wild-type mouse. Coinfected motor neurons will produce rabies viral particles to be transported across synapses to their premotor interneurons in the lumbar spinal cord and PPNs in the upper spinal cord. B, An image of a transverse lumbar spinal section after injection of TA muscle with rabies virus and AAV-G shows infected motor neurons and local premotor interneurons. A coinfected motor neuron is highlighted in the boxed area. C–G, High-magnification images show the marked motor neuron in B-expressing rabies protein (rabies-GFP), ChAT, and rabies glycoprotein mRNA. The section is counterstained with nuclei marker DAPI. H, I, Transverse sections from thoracic (H) and cervical (I) levels show rabies-GFP expressing long descending PPNs. The inset images in H and I are close-up views of the PPNs marked in the boxed area. CC, Central canal; Ipsi, ipsilateral side; Contra, contralateral side. Scale bars: B, 100 μm; C–G, 10 μm; H, I, 200 μm.
