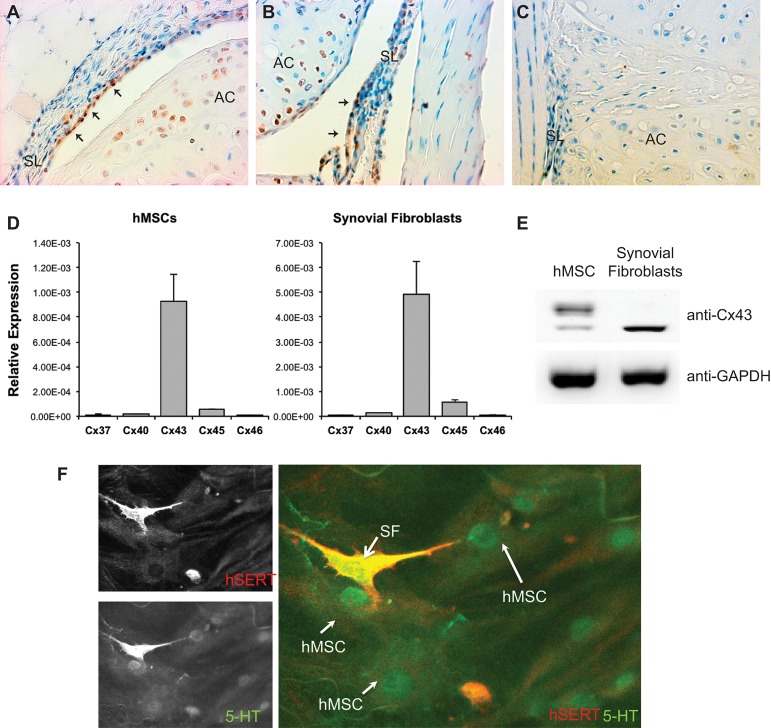
Fig 1. Cx43 is robustly expressed in synovial fibroblasts and hMSCs.
(A-B), Sections of murine knee joint were labeled with anti-Cx43 antibodies (brown). Cx43 is detected in the synovial fibroblasts (arrows) in the synovial lining (SL), as well as in the articular chondrocytes in the articular cartilage (AC). (C), A sections of murine knee joint were labeled with non-immune IgG as a negative control. (D), Quantitative real time RT-PCR was performed on RNA isolated from hMSCs and synovial fibroblasts in culture using primer pairs for the genes encoding Cx37, Cx40, Cx43, Cx45 and Cx46. Histograms indicate means ± standard deviation. (E), A western blot of whole cell extracts from hMSCs or synovial fibroblasts probed with anti-Cx43 antibodies reveals expression of Cx43 in both cell types. The expression of Cx43 in hMSCs is composed of a larger percentage of the higher molecular weight phosphorylated Cx43 than in SW982 cells, which express mostly the non-phosphorylated form. The images are from non-contiguous lanes of the same blot and exposure. GAPDH abundance was used as a loading control reference. (F) Immunofluorescnece microscopy reveals that hSERT+ SW982 cells (red) can take up serotonin/5-HT (green) and communicate it with hMSCs, indicating functional gap junctional communication between the two cell types. A representative image is shown.