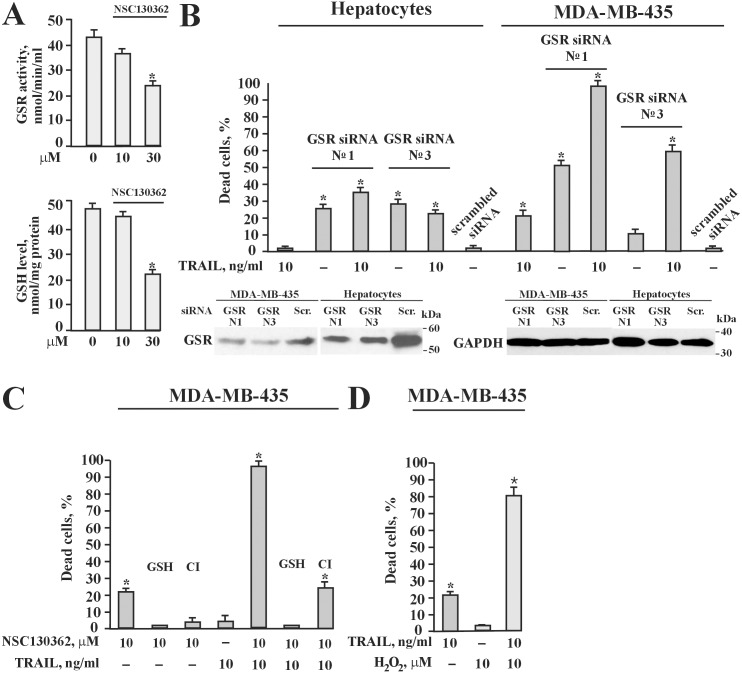
Fig 6.
(A) NSC130362 inhibited GSR activity (upper panel) and caused depletion of intracellular GSH (lower panel). MDA-MB-435 cells were treated with 30 μM of NSC130362 for 6 h and the levels of GSH and GSR activity were measured using GSH detection and GSR activity kits (Cayman), respectively. (B) upper panel, GSR siRNA potentiated TRAIL activity in MDA-MB-435 cells but not in human hepatocytes. MDA-MB-435 cells and human hepatocytes grown to subconfluency were transfected with GSR siRNA (10 nM/well) using SilentFect transfection reagent (BioRad). After 2 days, cells were treated with 10 ng/ml of TRAIL for an additional 24 h. Lower panel, Western blotting of GSR. Subconfluent cells were transfected with GSRsiRNA №1 and №3 as well as with scrambled siRNA (10 nM each) in a 6-well plate. Two days after transfection cells were lysed and the level of GSR was analyzed by Western blotting with the GSR antibodies and horseradish peroxidase-conjugated secondary antibodies. (C) GSH but not general caspase inhibitor Q-VD-OPh completely blocked NSC130362 activity. Subconfluent MDA-MB-435 cells in a 96-well plate were pre-incubated for 4 h with either GSH (10 mM) or general caspase inhibitor Q-VD-OPh (100 μM) (CI) followed by treatment with NSC130362 (10 μM) for 4 h and subsequent incubation with TRAIL (10 ng/ml) for an additional 24 h. (D) Hydrogen peroxide potentiated TRAIL activity in MDA-MB-435 cells. Subconfluent MDA-MB-435 cells in a 96-well plate were pre-incubated for 4 h with hydrogen peroxide (10 μM) followed by treatment with TRAIL (10 ng/ml) for an additional 24 h. At the end of all treatments, the ratio of dead cells was determined by an ATPLite reagent. *, P < 0.05.