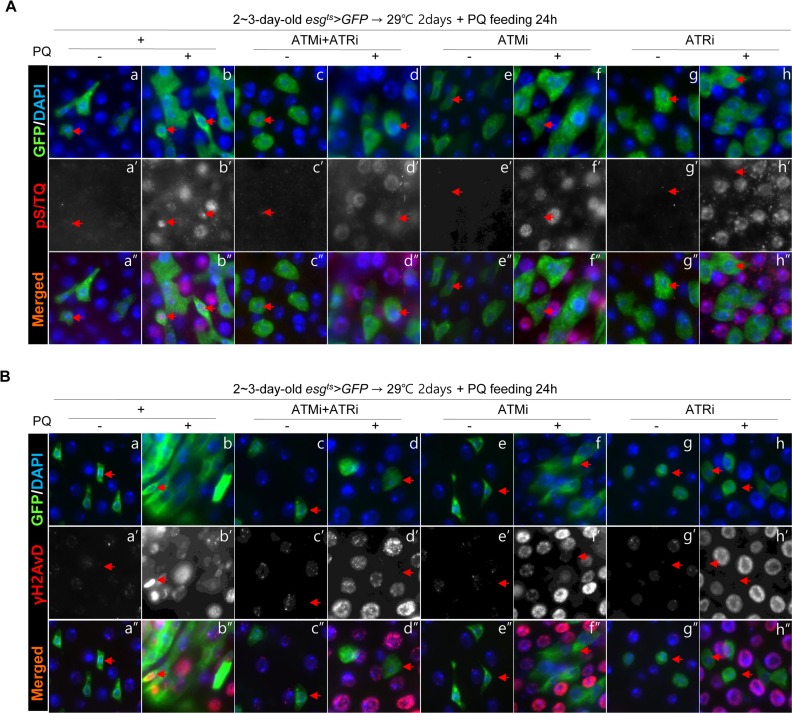
Figure 4. Effects of the intestinal stem cell (ISC)/enteroblast (EB)-specific knockdown of ATM or ATR on activation of the DNA damage response (DDR) by oxidative stress.
(A) Effects of the ISC/EB-specific knockdown of ATM, ATR, or both on the oxidative stress-induced increase of pS/TQ signals. The gut specimens of esgts>GFP, esgts>GFP+ATMi+ATRi, esgts>GFP+ATMi, and esgts>GFP+ATRi flies (kept at 29 °C for 2 days, with subsequent feeding on media containing 10 mM PQ for 1 day) were labeled with anti-pS/TQ (red) and anti-GFP (green) antibodies and 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI, blue). (B) Effects of the ISC/EB-specific knockdown of ATM, ATR, or both on the oxidative stress-induced increase of γH2AvD signals. The gut specimens of esgts>GFP, esgts>GFP+ATMi+ATRi, esgts>GFP+ATMi, and esgts>GFP+ATRi flies (kept at 29 °C for 2 days, with subsequent feeding on media containing 10 mM PQ for 1 day) were labeled with anti-γH2AvD (red) and anti-GFP (green) antibodies and DAPI (blue). Arrows indicate esg+ small cells. The original magnification is 400×.