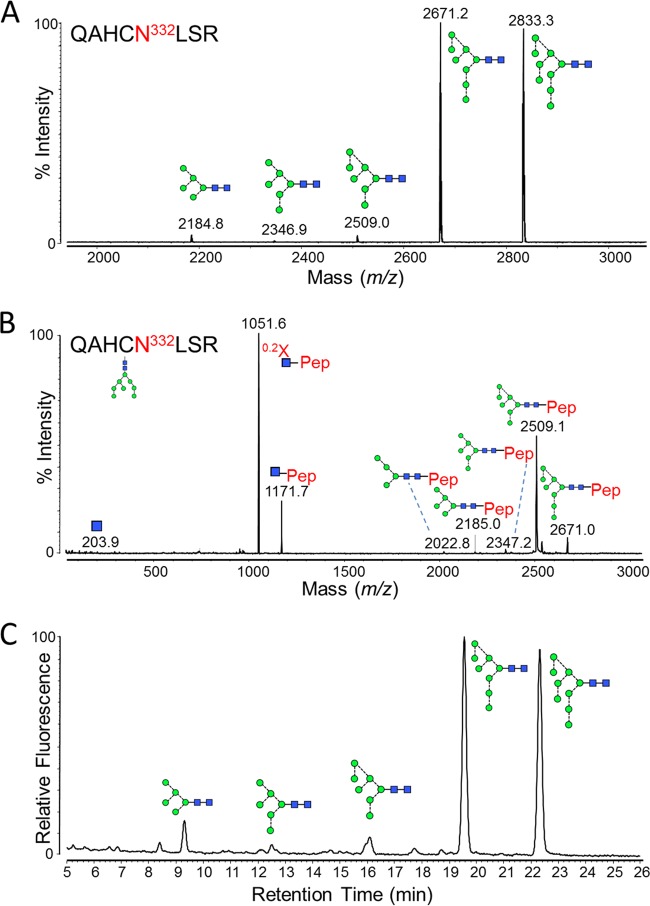
FIG 2.
Glycans present at the Asn332 glycosylation site. Recombinant, monomeric gp120BaL was expressed in HEK 293T cells from the pHLsec vector (41) and purified by metal-affinity and size exclusion chromatography, as previously described (42). gp120 was reduced, alkylated, and digested with trypsin (Promega), before fractionation using a Jupiter C18 5-μm 250- by 4.5-mm column (300-Å pore size) and a Dionex U3000 liquid chromatography system. Fractions were collected every minute, at a flow rate of 1 ml/min, for 90 min, and then analyzed on an Autoflex Speed MALDI tandem time of flight (TOF/TOF) instrument (Bruker), operated in positive-ion mode. (A) MALDI MS of pooled fractions containing the Asn332-containing glycopeptide, QAHCNLSR. The glutamine carried a pyro-Glu modification (−17), and the cysteine was modified due to treatment with iodoacetamide (carbamidomethyl, +57). Glycan structures corresponding to the observed glycopeptide masses are indicated. (B) MALDI MS/MS fragmentation spectrum of the 2,671.2 peak, corresponding to a Man8GlcNAc2 glycopeptide. Fragment ions were observed that were characteristic of glycopeptide MALDI MS/MS fragmentation (43), including [Mpep+H + 83]+ (corresponding to 0.2X-ring cleavage of the innermost GlcNAc) and [Mpep+H + 203]+ (corresponding to Y-type cleavage of the di-N-acetylchitobiose core). Y-type fragmentation of glycosidic bonds was also observed. (C) HILIC-UPLC profile of Asn332 glycans. Glycans were released from the QAHCNLSR glycopeptides by in-solution PNGase F (QA-Bio) digestion, according to the manufacturer's instructions, and then labeled using a LudgerTag 2-AB labeling kit (Ludger Ltd., Abingdon, United Kingdom). Chromatography was performed on a Waters Acquity UPLC instrument. Glycans were assigned by comparison with known oligomannose-type glycan standards (Ludger Ltd., Abingdon, United Kingdom).