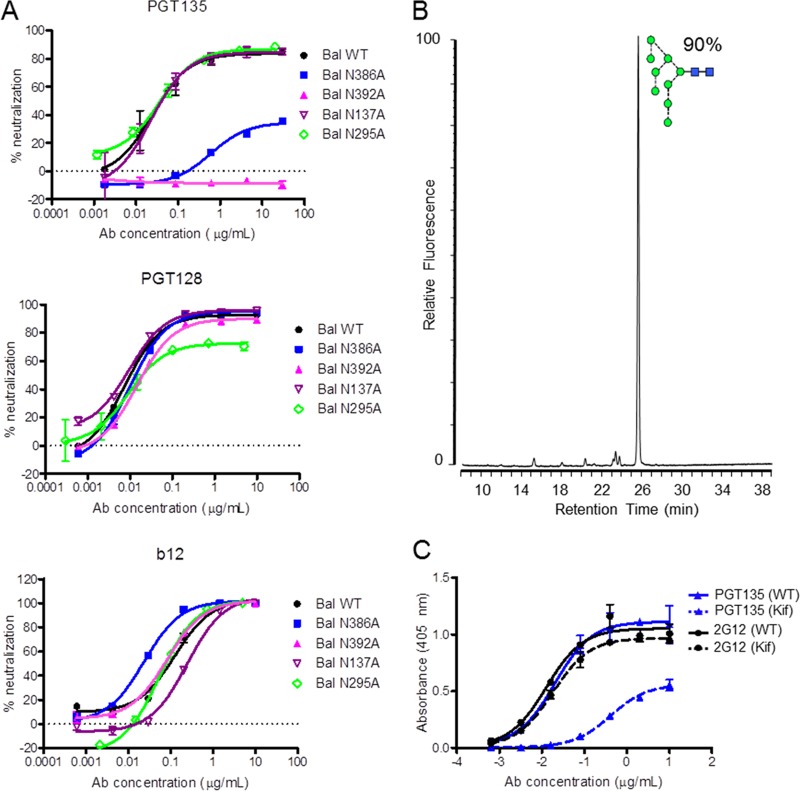
FIG 4.
Influences of gp120 glycans on bnAb recognition. (A) Neutralization sensitivity of PGT135, PGT128, and b12 against BaL wild-type pseudovirus and glycan site mutants. bnAbs PGT128 and b12 are used as controls. To produce pseudoviruses, plasmids encoding Env were cotransfected with an Env-deficient genomic backbone plasmid (pSG3ΔEnv) in a 1:2 ratio with the transfection reagent polyethyleneimine (PEI) (1 mg/ml, 1:3 PEI-total DNA [Polysciences]) into HEK 293T cells. Pseudoviruses were harvested 72 h posttransfection. Neutralizing activity was assessed using a single-round replication pseudovirus assay with TZM-bl target cells, as described previously (2). Glycan sites N137, N295, N386, and N392 were removed using site-directed mutagenesis through an Asn-to-Ala mutation. Mutations were verified by DNA sequencing (MWG Eurofins, Germany). (B) Glycan profile of recombinant gp120 expressed in HEK 293T cells in the presence of kifunensine, analyzed as described in the legend to Fig. 2C. (C) Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) data of PGT135 (blue) and 2G12 (black) binding to wild-type (continuous line) and kifunensine-treated (dashed line) gp120. ELISAs were performed as previously described (34).