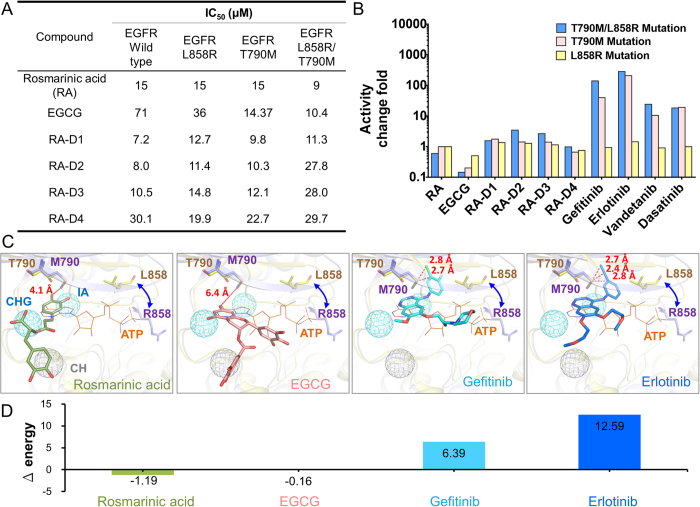
Figure 5. Type-C inhibitors against drug-resistant EGFR.
(A) IC50 values of type-C inhibitors against wild-type, T790M, L858R, and T790M/L858R mutant EGFR. (B) Fold changes in activity of rosmarinic acid, EGCG, gefitinib, erlotinib, vandetanib, and dasatinib in the presence of the drug-resistant mutations. (C) Binding modes of type-C inhibitors and kinase drugs in the T790M/L858R mutant EGFR. The kinase-drug complex structures and the mutant EGFR structure (PDB 3W2P) are superimposed on the structure of wild-type EGFR, including EGFR-gefitinib (PDB 2IVT) and EGFR-erlotinib (PDB 1M17) complex structures. (D) Energy difference of the compounds between the wild-type (T790) and mutant (M790) residues calculated by GEMDOCK. Type-C inhibitors maintain similar interaction energy for the mutant residue, whereas gefitinib and erlotinib lose interactions when the mutation occurs.