FIG 5.
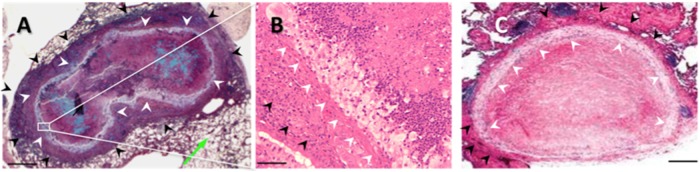
(A) Movat staining of a mouse (CBA/J) lung cryptococcal granuloma infected with C. neoformans Δgcs1. White arrowheads, the ring of multinucleated macrophages containing the C. neoformans cells (blue) in a necrotic center; green arrow, normal lung tissue; black arrowheads, ring of fibrotic tissue with a lymphocyte and neutrophil component. (B) H&E staining of the granuloma in panel A showing the macrophage ring (white arrowheads) and neutrophils and lymphocytes (black arrowheads). Histology sections were prepared at the end of the experiment (60 days postinfection). (C) H&E staining of a human lung cryptococcal granuloma showing a similar ring of multinucleated macrophages. (From the New England Journal of Medicine, R. M. Fairhurst and D. A. Pegues, Pulmonary cryptococcal granulomas, vol. 347, p. 497, Copyright 2002 Massachusetts Medical Society. Reprinted with permission from Massachusetts Medical Society.) Bars = 200 μm (A and C) and 50 μm (B).
