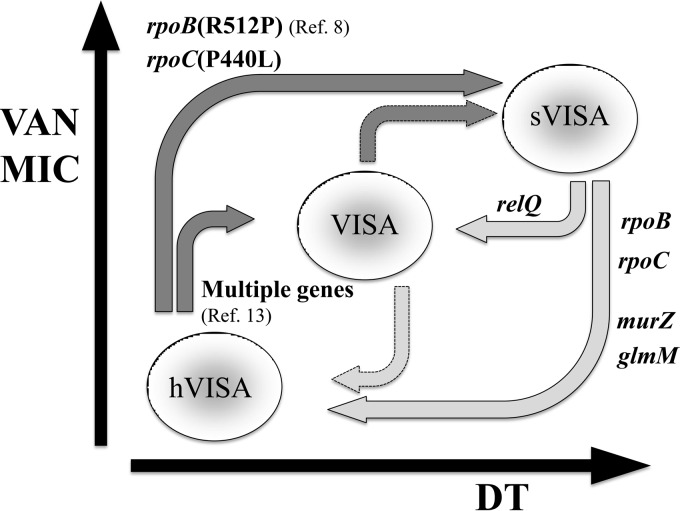
FIG 5.
Reciprocal relationship between vancomycin (VAN) MICs and doubling times (DTs) of hVISA, VISA, and sVISA strains. The hVISA strain generates VISA and sVISA strains following exposure to VAN. The sVISA strain has a higher VAN MIC and extremely prolonged DT. This step was associated with the mutations rpoB(R512P) and rpoC(P440L). The sVISA phenotype is stable in the presence of VAN but rapidly reverts to VISA and hVISA phenotypes in antibiotic-free media. The ability to revert is associated with mutations in peptidoglycan synthesis genes and the relQ gene and alternative mutations in rpoB and/or rpoC genes. Deep gray and pale gray arrows indicate the presence and absence of VAN, respectively.