Figure 1.
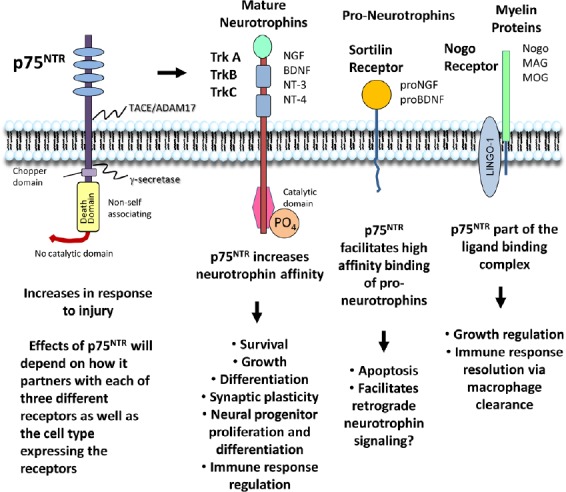
Potential signaling partners of the p75 neurotrophin receptor (p75NTR) following nervous system injury.
The p75NTR is a single membrane-spanning receptor in the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) death domain containing receptor family. Four cysteine-rich extracellular domains bind each of the four neurotrophins: NGF, BDNF, NT-3 or NT-4 with low affinity and their respective pro-forms with high affinity. The intracellular portion of the receptor does not contain a catalytic domain to autoactivate the receptor. Thus, the receptor functions largely via interactions with other effector proteins. The p75NTR can interact with at least three different receptor classes which mediate different outcomes: Trk receptors, sortilin and Nogo receptor. 1) The p75NTR-Trk receptor complex increases the affinity of the mature neurotrophin/Trk interaction and enhances pro-survival and growth signaling via PI3KAkt, ERK or PLCγ pathways. In addition, expression on neural progenitors supports proliferation and differentiation. 2) Interactions of p75NTR with sortilin allow high affinity binding of the pro-neurotrophins to the p75NTR/sortilin complex leading to apoptosis. However, the role of sortilin may be diverse as it also supports neuron survival via its prominent sorting functions which include anterograde trafficking of neurotrophin receptors. 3) Interactions of the p75NTR with the Nogo receptor and Lingo-1 play a role in the control of growth. Binding of myelin proteins to the complex activates RhoA by displacement of Rho-GDI and concurrently suppress Rac leading to collapse of growth cones, neurite retraction and decreases in spine density. These various interactions afford the p75NTR the capacity to play a pivotal role in the regulation of numerous processes that determine the fate and functions of the cell. The role of the p75NTR in response to injury is largely unknown and is a potential source of new strategies to facilitate recovery of the damaged nervous system. NGF: Nerve growth factor; BDNF: brain-derived neurotrophic factor; NT-3: neurotrophin-3; NT-4: neurotrophin-4; Trk: tropomyosin regulated kinase; ERK: extracellular signal-regulated kinase; PLCγ: phospholipase C-γ.
