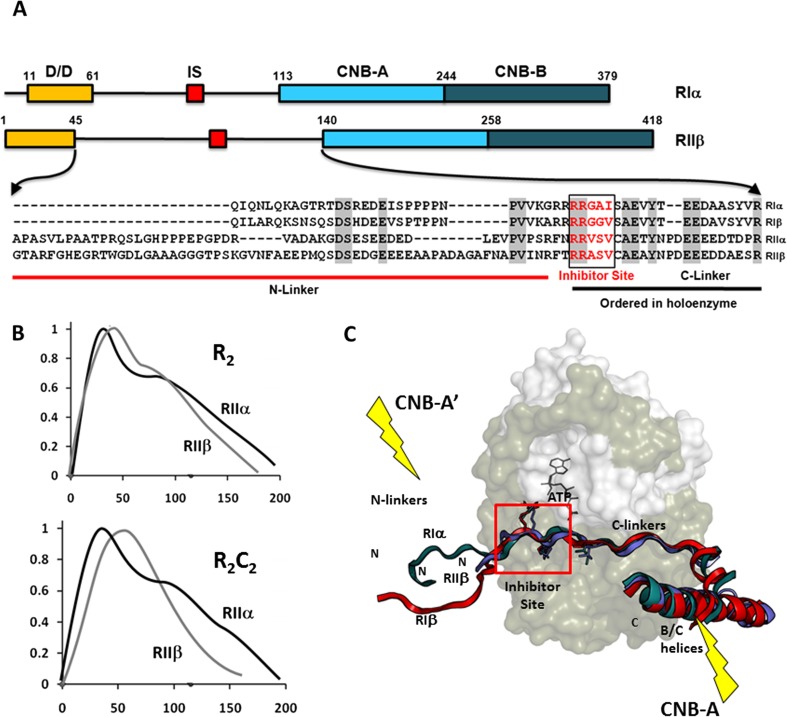
Fig. 1.
Organization of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA) R-subunits. a The organization of the RIα and RIIβ regulatory (R)-subunits and the sequence of the linker regions for all four isoforms are shown. b Small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) profiles of the PKA RII-homodimers and holoenzymes show the isoform differences. c Following binding to the catalytic (C)-subunit, the Inhibitor Site docks at the active site cleft of the C-subunit (red box) and the C-linker becomes ordered. The N-linker plays an important role in defining the quaternary structure of each holoenzyme and is ordered differently in the RIα-, RIβ- and RIIβ-subunits following their binding to the C-subunit. This isoform-specific positioning of the N-linker contributes in unique ways to the organization of each tetrameric holoenzyme. Highlighted are the positions of the two symmetry related cyclic nucleotide binding (CNB)-A domains in the same holoenzyme. Each CNB-A domain also allosterically regulates the adjacent C-subunit in the holoenzyme