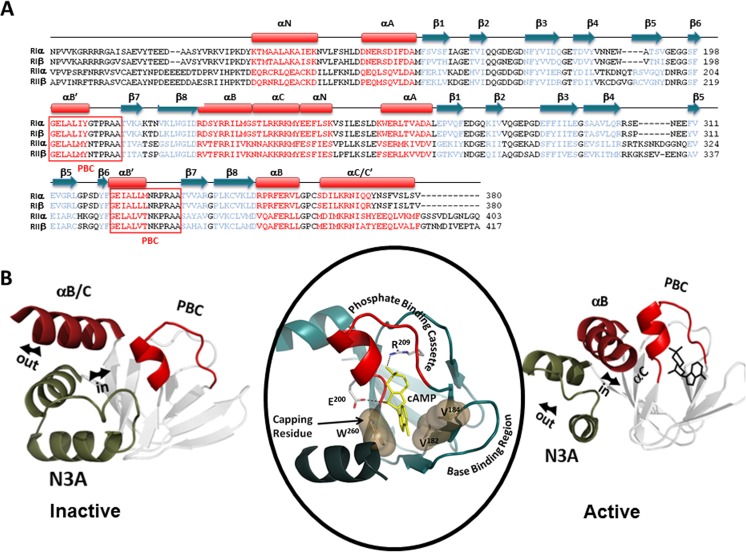
Fig. 2.
CNB domains of R-subunits. a Sequence alignments of the R-subunits C-linker and CNB domains (red helices, blue strands). b The CNB-A domain of RIα is used as a prototype for this highly conserved structural domain. C-subunit-bound Inactive (H conformation) and cAMP-bound Active (B conformation) (PDB ID 1CX4) conformations are shown. In the absence of cyclic AMP (cAMP) (left), the B/C helix moves ‘out’, while the N3A motif moves ‘in.’ Upon cAMP binding (right), the phosphate binding cassette (PBC) moves towards the cAMP phosphate, moving the B/C-helix ‘in’ and causing the N3A motif to move ‘out.’ Middle panel shows how the cyclic nucleotide is bound to the PBC, which is the signature motif for this domain