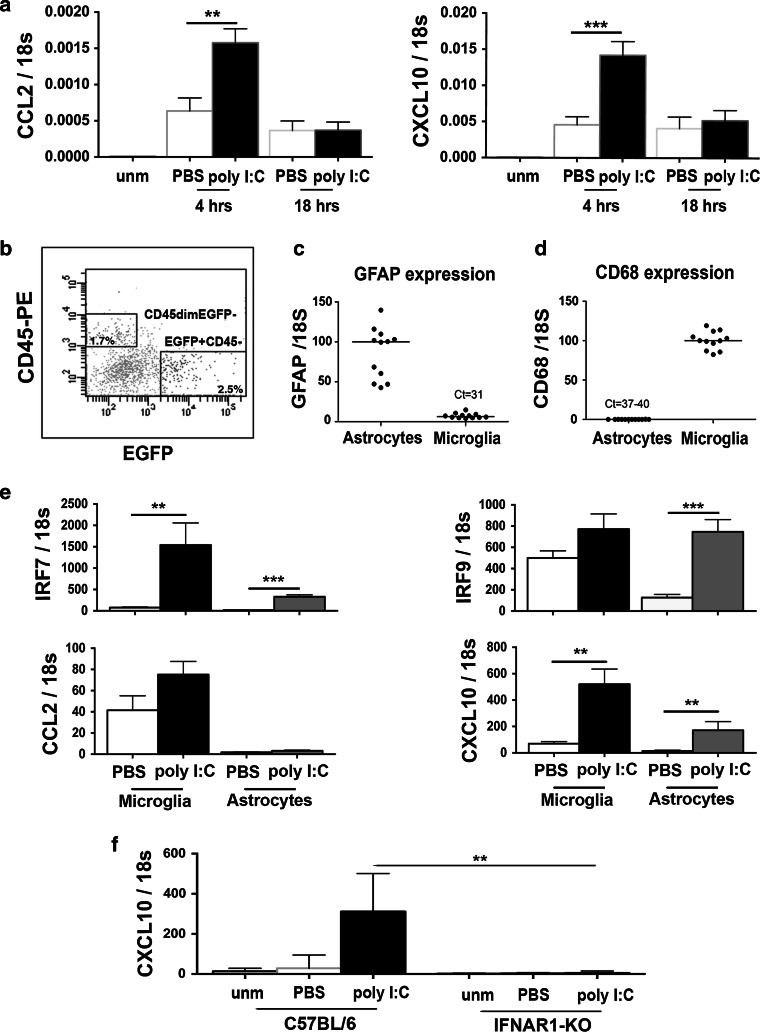
Fig. 6.
Intrathecal induction of IFN-β induced response in microglia and astrocytes. a Mice with EAE had elevated levels of CCL2 and CXCL10 compared to unmanipulated (unm) mice. Intrathecal administration of poly I:C transiently induced both CCL2 and CXCL10 gene expression in CNS. Expression was highest at 4 h, and reduced to levels corresponding to levels in control mice, at 18 h. b Representative flow cytometry profiles for cells isolated from EGFP-GFAP mice. Microglia and astrocytes were sorted as CD45dimEGFP− and CD45−EGFP+ cells, respectively. Sorted astrocytes and microglia were validated by analysis of expression of marker genes GFAP (c) and CD68 (d), respectively. Number of mice for flow cytometry was between 6 and 12 in each group, and the experiment was repeated three times independently. e Intrathecal injection of poly I:C induced upregulation of IRF7 in both microglia and astrocytes. Sorted microglia from naïve mice expressed endogenously higher levels of IRF9 mRNA than astrocytes. Poly I:C induced IRF9 in astrocytes, not in microglia. Sorted microglia from naïve mice expressed endogenously higher levels of CCL2 mRNA than astrocytes. In microglia and astrocytes poly I:C did not induce changes in CCL2 mRNA expression, but induced increased CXCL10 in both microglia and astrocytes. f The upregulation of CXCL10 mRNA in response to poly I:C was IFNAR1 dependent. Data were analyzed by two-tailed nonparametric Student’s t test followed by Mann–Whitney test. Results are presented as mean ± SEM, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001