Figure 8.
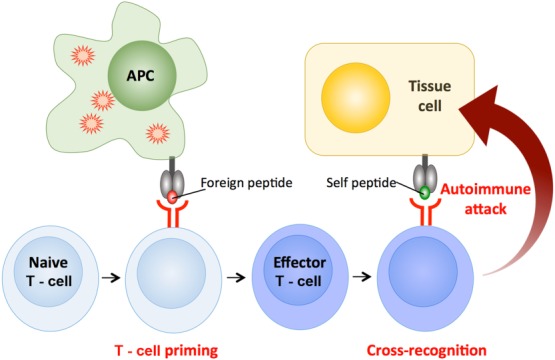
T cell cross-reactivity causes autoimmunity. T cells bearing autoreactive T cell receptors (TCRs) sometimes escape from thymic culling and populate the peripheral tissues. Such cells usually bear TCRs that bind very weakly to self-peptide and generally remain harmless. However, if such a T cell becomes activated in response to a pathogen-derived peptide it will be stimulated to become an effector T cell. Antigen-experienced cells are known to be more sensitive to TCR triggering. Activation of such cells by a cross-recognized self-peptide could then result in autoimmune attack.
