Figure 4.
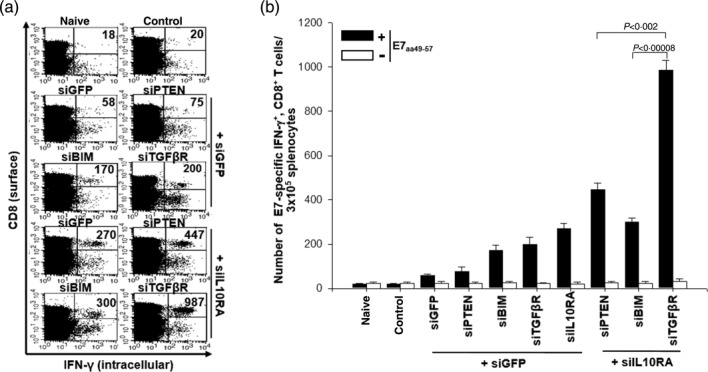
Vaccination with dendritic cells (DCs) transfected with various small interfering RNA (siRNA) increases the number of E7-specific CD8+ T cells. (a) Intracellular cytokine staining and flow cytometry analysis to determine the number of interferon (IFN)-γ-producing E7-specific CD8+ T cells in mice after immunization with E7 peptide-pulsed DCs transfected with various siRNA constructs. Mice (five per group) were vaccinated twice with E7 peptide-pulsed DCs transfected with siRNA targeting green fluorescent protein (GFP), phosphatase and tensin homologue deleted on chromosome 10 (PTEN), Bcl-2-like protein 11 (BIM) interleukin (IL)-10RA, transforming growth factor (TGF)-βR, IL-10RA+PTEN, IL-10RA+BIM or IL-10RA+TGF-βR. There was a 1-week interval between injections of the transfected DCs for the purpose of vaccination. Splenocytes were harvested 1 week after the last vaccination, stained for CD8+ and IFN-γ, and analysed by flow cytometry to detect activated E7-specific CD8+ T cells. Representative flow cytometry data for splenocytes harvested from the vaccinated mice and stimulated with E7 aa49-57 peptide or without peptide stimulation. The naive group has non-transfected DCs without E7 peptide pulsing, while the control group has siGFP transfected DC without E7 peptide pulsing. (b) The bar graph indicates the number of IFN-γ-expressing E7-specific CD8+ T cells per 3 × 105 splenocytes from vaccinated mice (mean ± standard deviation). The data presented in this figure are representative of two independent experiments.
