Fig. 8.
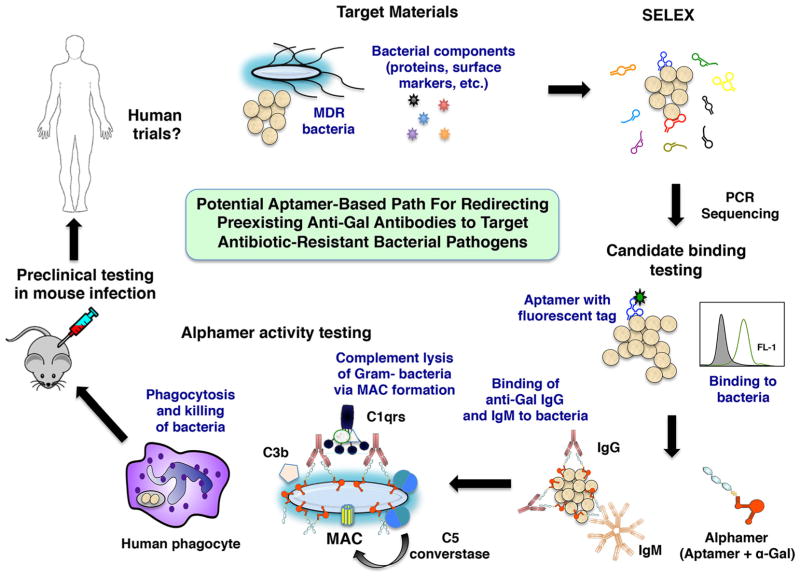
Summary scheme for characterizing aptamer-based drugs. In a process termed Systematic Evolution of Ligands by Exponential Enrichment (SELEX), bacterial whole cells or bacterial components, aptamer libraries, PCR, and sequencing are used to identify aptamer candidates for further characterization. Fluorescently tagged aptamer candidates are synthesized and prioritized based on their binding to several strains of the target bacterial species by flow cytometry. Then, alphamer versions of prioritized aptamers are prepared. After confirmation that the alphamers bind to bacteria and attract anti-Gal antibodies to the microbial surface, alphamer activity is tested in correlate of protection assays in vitro (complement deposition and lysis, phagocytosis assays) that may predict the in vivo activity of candidate molecules. Alphamers with strong in vitro activity could then be tested in mouse infection models and later in humans