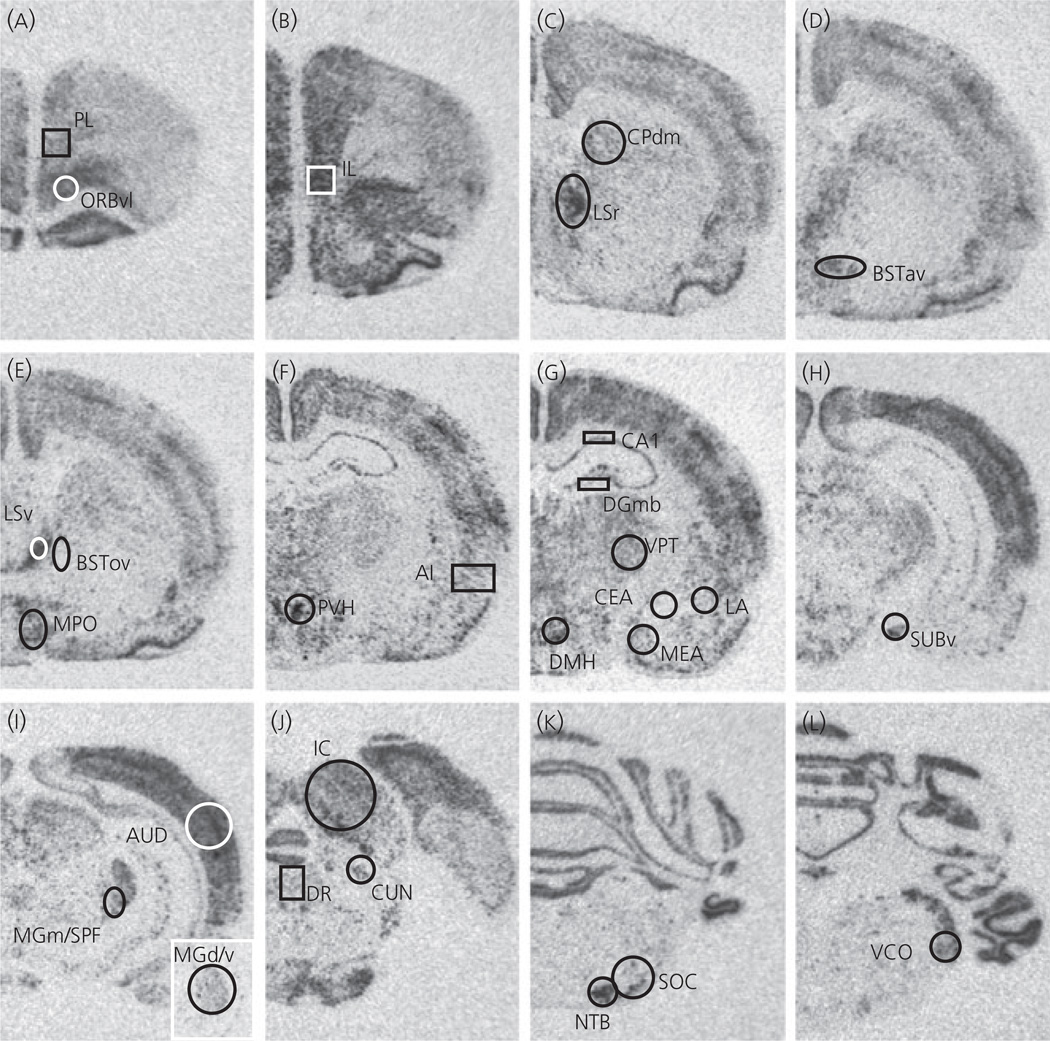
Fig. 7.
Photomicrographs showing c-fos mRNA expression after 30 min exposure to 85 dBA noise (Experiment 6), in a rat housed under sedentary conditions for 6 weeks. Templates used for semi-quantitative analysis are shown for (a) prelimbic cortex (PL) and ventrolateral orbitofrontal cortex (ORBvl); (b) infralimbic cortex (IL); (c) dorsomedial caudate putamen (CPdm) and rostral lateral septum (LSr); (d) anteroventral area of the anterior bed nucleus of the stria terminalis (BSTav); (e) ventral lateral septum (LSv), oval nucleus of the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis (BSTov) and medial preoptic area (MPO); (f) paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus (PVH) and agranular insular cortex (AI); (g) CA1 region of the hippocampus (CA1), medial blade of the anterior dentate gyrus (DGmb), ventral posterior thalamus (VPT), central nucleus of the amygdala (CEA), lateral nucleus of the amygdala (LA), medial nucleus of the amygdala (MEA) and dorsomedial nucleus of the hypothalamus (DMH); (h) ventral subiculum (SUBv); (i) auditory cortex (AUD) and medial division of the medial geniculate complex with subparafascicular nucleus of the thalamus, parvocellular part (MGm/SPF). The insert is taken at a more rostral region of the medial geniculate complex to show the dorsal/ventral region analysed (MGd/v); (j) inferior colliculus (IC), dorsal raphe nucleus (DR) and cuneiform nucleus (CUN); (k) nucleus of the trapezoid body (NTB) and superior olivary complex (SOC); (l) ventral cochlear nucleus (VCO).