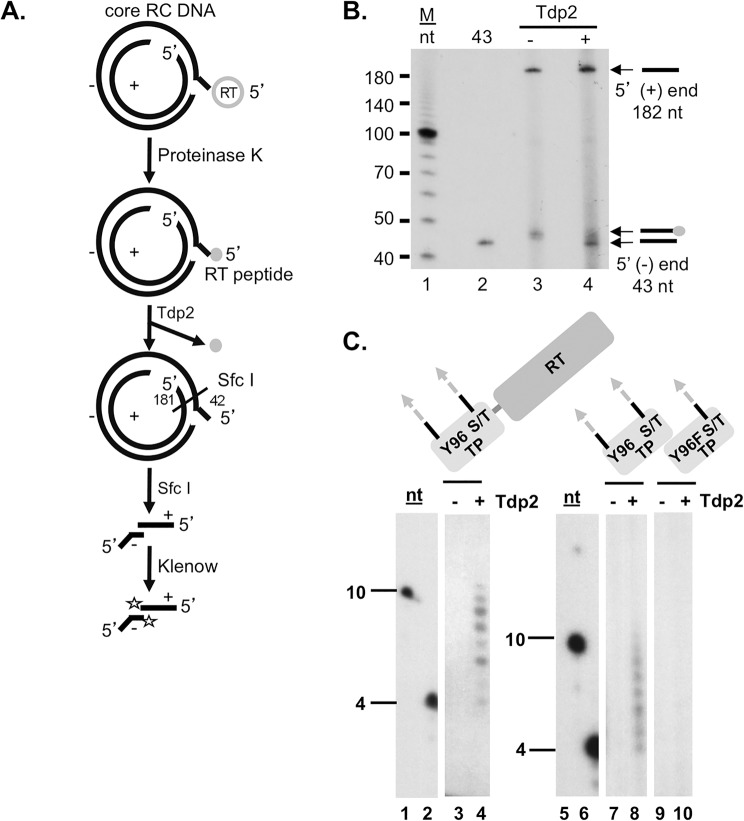
Fig 1. Tdp2 cleavage of the covalent linkage between the RT protein and the 5’ end of the viral minus strand DNA.
(A) and (B). Tdp2 removal of proteinase K-derived RT peptide from the 5’ end of core RC DNA. (A) Diagram of the Tdp2 cleavage reaction and detection of the cleavage product derived from the HBV RC DNA. HBV DNA extracted from cytoplasmic nucleocapsids (core) with proteinase K digestion was treated with Tdp2, followed by Sfc I digestion and labeling with [α-32P]-TTP using Klenow fill-in reaction. Proteinase K generated RT peptide is indicated by a small shaded circle. The restriction endonuclease Sfc I cuts near the 5’ end of the (-) strand DNA, within the cohesive overlap of RC DNA, generating fragments containing short 5’ (-) and (+) DNAs 42 and 181 nt (the RNA primer being removed by prior RNase digestion) in length, respectively, as indicated. A single radiolabeled TMP added by Klenow to the 3’-recessed ends of the Sfc I-generated core RC DNA fragments are indicated by the stars. (B) Klenow-labeled products were resolved by urea-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) and visualized by autoradiography. The 5’ ends of the (+) and (-) strand of core RC DNA are indicated by arrows as are the 5’ end of the (-) strand with or without the residual RT peptide. The lane labeled as “43” contained a DNA oligonucleotide having the same sequence as the first 43 nt of the HBV (-) strand DNA and labeled at the 5’ end by using T4 ploynucleotide kinase and [γ-32P]-ATP. (C). Tdp2-mediated cleavage of DHBV RT-DNA linkages generated in vitro. MiniRT2 protein priming reactions carried out in the presence of Mn2+, [α-32P]-dGTP and unlabeled dATP, dCTP, dTTP, were mock treated (-) or treated (+) with Tdp2 (lanes 3 and 4). TP, either WT (lanes 7 and 8) or Y96F mutant (lanes 9 and 10), was mixed with the polymerase domain for trans-complementation priming reaction in the presence of Mn2+, [α-32P]-dGTP and unlabeled dATP, dCTP, dTTP. The reactions were mock treated (-) or treated (+) with Tdp2 (lanes 7–10). Reaction products from mock treated (-) or Tdp2-treated (+) protein priming reactions were resolved by urea-PAGE and detected by autoradiography. Lanes 1, 2, 5, and 6 show the 10 and 4 nt DNA marker. Domain diagrams of MiniRT2, TP and its mutant derivative Y96F-TP are depicted above each panel with the primer residue Y96 or F substitution indicated. The DNA oligomers covalently attached to the MiniRT2 protein or the TP domain are highlighted by the shaded and dotted arrows extending from the protein. Cryptic serine and threonine (S/T) residues that can serve as priming sites under Mn2+ conditions, as well as the authentic Y96 site, are highlighted.