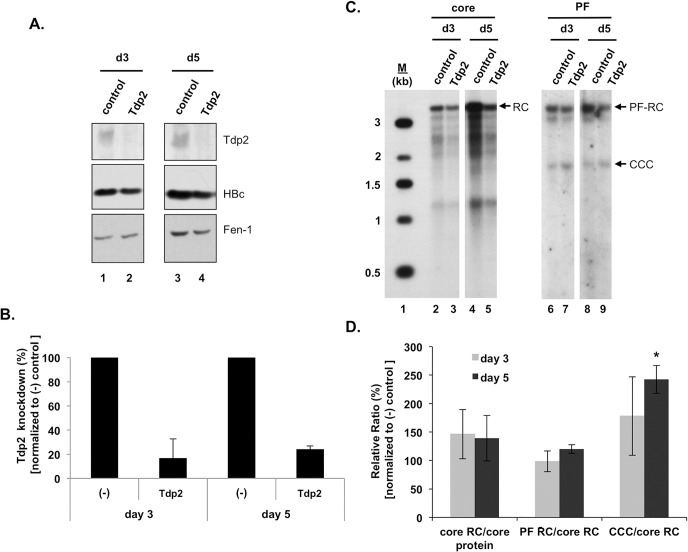
Fig 3. Knockdown of Tdp2 was associated with an increase in HBV CCC DNA.
HBV replication was induced in HepAD38 cells by removal of tetracycline from the culture medium. Cells were transfected 4 days after tetracycline removal with control (Non-target) or Tdp2-specific siRNA. Viral DNA levels were measured 3 and 5 days post-siRNA transfection. (A) Tdp2 and HBV core protein levels were measured by western blot analysis. Fen-1 was used as a loading control. (B) Percent Tdp2 knockdown at day 3 and 5 post-siRNA transfection relative to control siRNA knockdown (set to 100%). (C) HBV DNAs were extracted from the cytoplasmic nucleocapsid (core) with protease digestion or the Hirt supernatant without protease digestion (PF) and analyzed by Southern blotting. (D) Quantitative analysis of HBV DNA replication. The indicated viral DNA ratios following Tdp2 knockdown were normalized to the corresponding DNA ratios after control (Non-target) treatment (set to 100%) and are reported as the mean relative ratios ± standard error of the mean of three independent experiments. The asterisk indicates a significant difference in Tdp2 knockdown CCC/core RC compared to control conditions at day 5 post-siRNA transfection (P < 0.05; unpaired, two-tailed t-test). CCC, CCC DNA; PF-RC, PF-RC DNA; RC, RC DNA.