Figure 1.
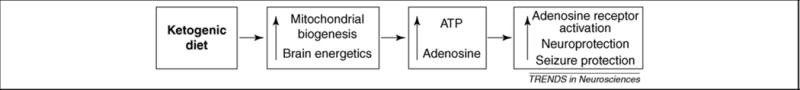
A purinergic signaling hypothesis for the neuroprotective and antiseizure actions of the ketogenic diet. During maintenance on a ketogenic diet, increased mitochondrial biogenesis, brain energetics and brain ATP levels are observed. Increased intracellular ATP enhances brain energy stores and homeostasis, and increased extracellular ATP is rapidly dephosphorylated into extracellular adenosine with subsequent signaling through adenosine receptors. Adenosine, acting at adenosine A1 receptors, exerts an inhibitory and anticonvulsant influence thereby providing neuroprotection and antiseizure effects. Enhanced signaling although A1 receptors provides a mechanism directly linking cellular energy molecules (ATP and adenosine) with decreased neuronal activity (A1 receptor activation).
