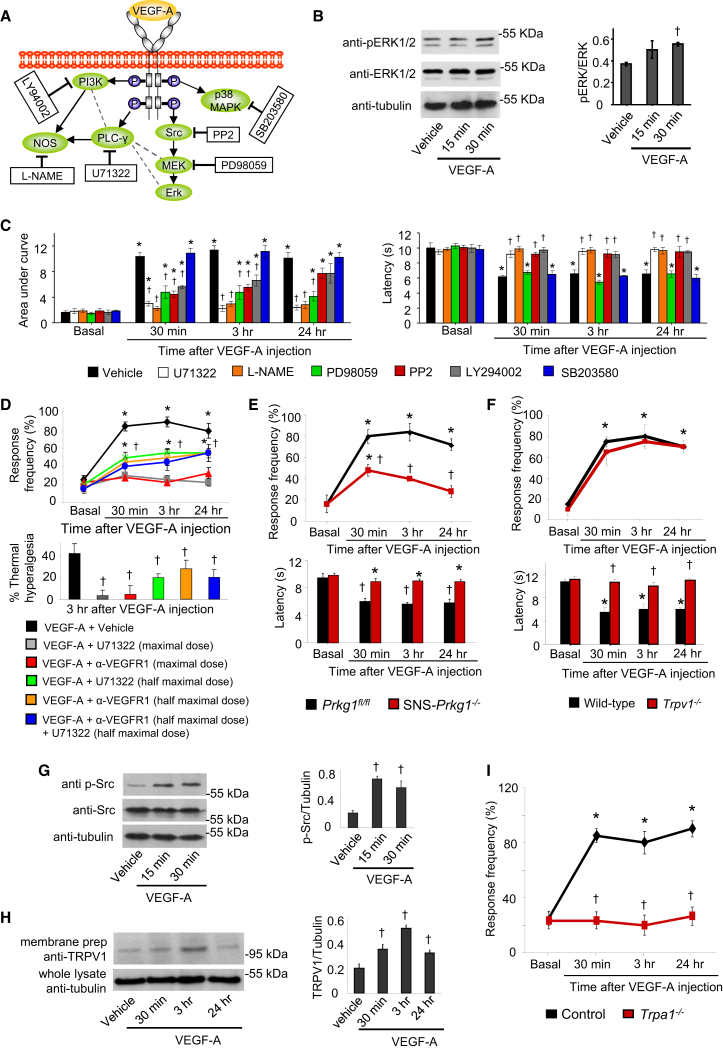
Figure 3.
Signaling Pathways Underlying Nociceptive Sensitization by VEGF-A
(A) A schematic overview of intracellular signaling mediators activated by VEGFRs (in oval symbols) and their respective pharmacological inhibitors in square boxes.
(B) Western blots showing VEGF-A-induced phosphorylation of ERK1/2 in neuron-enriched cultured DRG neurons (n = 3 independent experiments).
(C) Effects of hind-paw injection of pharmacological inhibitors on mechanical hypersensitivity (left) and thermal hypersensitivity (right) evoked by intraplantar injection of VEGF-A (1 ng). Shown are effects following single-dose intraplantar injection: L-NAME (18.5 nmoles, NOS inhibitor), U71322 (20 pmoles, PLCγ inhibitor), LY294002 (1 nmole, PI3K inhibitor), PP2 (200 pmoles, Src Kinase inhibitor), PD98059 (18.7 nmoles, MEK inhibitor), SB203580 (30 nmoles, p38 MAPK inhibitor), vehicle (1% DMSO).
(D) Experiments comparing the above data with effects of intraplantar combinations of half-maximal doses of PLCγ inhibitor and anti-VEGFR1 antibody on VEGF-A-induced mechanical hypersensitivity to 0.4 g von Frey force (upper) and thermal hyperalgesia (lower).
(E and F) Effects of VEGF-A (1 ng, intraplantar) in mice lacking Prkg1 selectively in nociceptive neurons of the DRG (SNS-Prkg1−/− mice; E) or in mice lacking Trpv1 (Trpv1−/− mice; F) (n = 6–8 mice/group).
(G) Western blots on Src phosphorylation in DRG cultures (three independent experiments).
(H) TRPV1 expression in membranes of distal branches of sciatic nerve in mice receiving intraplantar injections of VEGF-A or vehicle (n = 3 mice/group).
(I) Effects of VEGF-A (1 ng, intraplantar) in mice lacking Trpa1 (Trpa1−/− mice) (n = 8 mice/group).
∗p < 0.05 as compared with basal value, †p < 0.05 as compared with corresponding control, ANOVA followed by post hoc Fisher’s test. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. See also Figure S3.