Fig. 1.
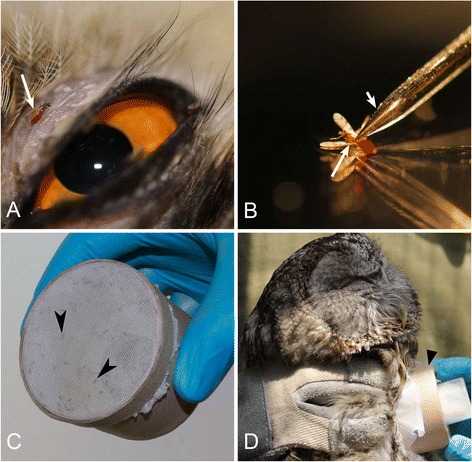
Experimental infection (a, c, d) and dissection (b) of the biting midges Culicoides impunctatus (a, b) and Culicoides nubeculosus (c, d) for detection of sporogonic stages of owl Haemoproteus spp. a – engorged biting midge C. impunctatus (long arrow) taking blood meal close to an eye of the long-eared owl Asio otus; b – dissection of C. impunctatus, short arrow indicates a dissecting needle; c – a hand-held cardboard box with a colony of C. nubeculosus inside, arrowheads indicate the midges sitting on fine-mesh bolting silk covering one side of the box; d – experimental infection of the colony of C. nubeculosus midges by means of adherence of a box with flies to skin of the tawny owl Strix aluco, triangle arrowhead indicates the box with flies
