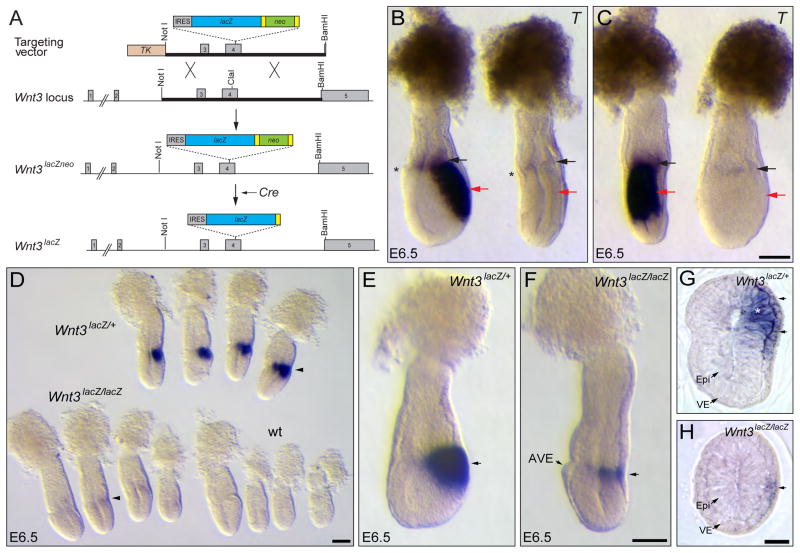
Figure 1. Visceral endoderm Wnt3 regulates its own expression in the epiblast.
A. Schematic representation of the strategy for the generation of Wnt3lacZNeo and Wnt3lacZ alleles. A replacement vector carrying an IRES-lacZ-loxP-Neo-loxP cassette inserted into the ClaI site of exon 4 was used to generate Wnt3lacZNeo/+ mice. Heterozygous Wnt3lacZNeo/+ mice were crossed to Sox2Cre mice to remove the Neo cassette and generate Wnt3lacZ/+ animals. B, C. Lateral (B) and posterior (C) view of the same control and Wnt3lacZ/lacZ mutant embryos hybridized with T The Wnt3lacZ/lacZ mutant embryo lacks expression of T in the epiblast (red arrows). Faint T expression is observed in the extra-embryonic ectoderm of the mutant embryo (black arrows). The mutant embryo shows the characteristic flattened anteroposterior morphology of Wnt3 null embryos, indicating that Wnt3lacZ is a null allele. The anterior visceral endoderm (AVE), indicating the anterior side of the embryo, is marked with an asterisk. D. Analysis of β-galactosidase activity in embryos derived from Wnt3lacZ/+ heterozygous crosses at E6.5. Strong staining is observed in the posterior region of heterozygous (Wnt3lacZ/+) embryos, while only weak staining is observed in mutant (Wnt3lacZ/lacZ) embryos (arrowheads) and no staining in wild-type (wt) embryos. E, F. Wholemount β-galactosidase activity assay of heterozygous (E) or homozygous (F) embryos for Wnt3lacZ alleles dissected at a slightly older stage than those shown in D. In the homozygous embryo, β-galactosidase activity is restricted to a narrow band on the posterior side (arrow) opposite to the AVE. G, H. Cross sections of heterozygous (G) and mutant (H) Wnt3lacZ embryos assayed for β-galactosidase activity. Heterozygous embryos show β-galactosidase activity in the epiblast (asterisk) and visceral endoderm (arrows), whereas mutant embryos exhibit staining only in the visceral endoderm (arrow). IRES, internal ribosomal entry site. TK, Thymidine Kinase cassette; Yellow rectangles represent loxP sites. Epi, epiblast; VE, visceral endoderm. Panels B and C, E and F and G and H are shown at the same scale. Scale bars, 100 μm in C, D, F and H.