Fig. 1.
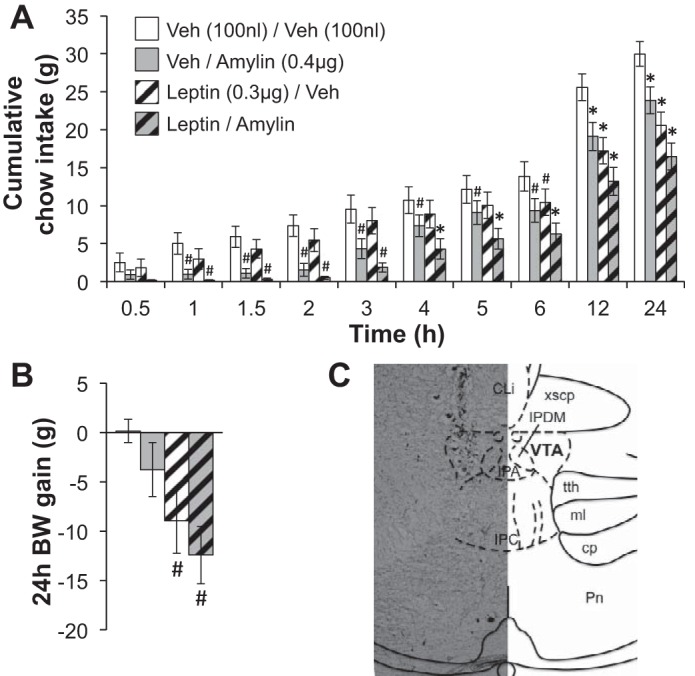
Cumulative food intake and 24-h body weight (BW) gain after intra-ventral tegmental area (VTA) administration of suprathreshold doses of amylin (0.4 μg) or its vehicle [Veh; 100 nl of artificial cerebrospinal fluid (aCSF)] plus leptin (0.3 μg) or its Veh (100 nl of 0.01 M sodium bicarbonate). A: VTA delivery of amylin alone or leptin alone reduces chow intake, but the suppression of feeding produced by the combination of amylin and leptin is greater than the effect of either peptide alone. B: the combination of amylin and leptin also significantly reduces body weight gain. Within a time bin: #statistical significance (P < 0.05) compared with Veh/Veh; *significant difference (P < 0.05) from all other conditions. All data shown as means ± SE. C: a representative image of VTA injection placement (30-μm coronal section) is shown.
