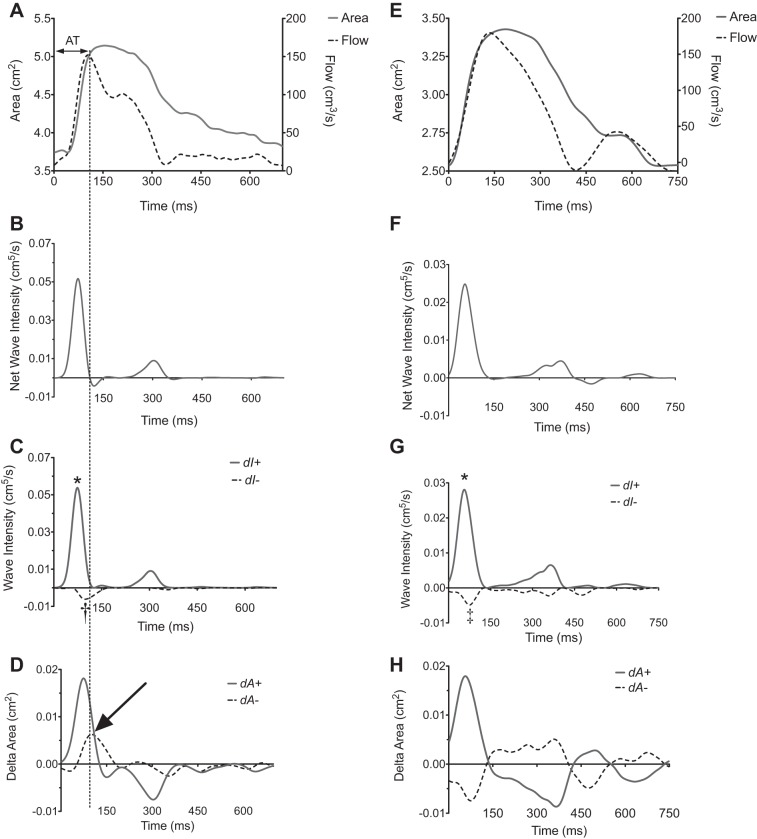
Fig. 1.
Wave intensity analysis (WIA) in representative pulmonary hypertension (PH) patient (A–D) and control (E–H). Three types of waveforms were found to arise during early and mid systole in study participants using wave separation analysis: 1) a forward compression wave: characterized by increasing area and increasing flow representing cardiac ejection (* in C and G); 2) a backwards compression wave: increasing area [pressure] and decreasing flow († in C); and 3) backwards expansion wave: decreasing area [pressure] and/or increasing flow (‡ in G). The identification of the backwards compression and expansion waves can be seen from examination of D and H, showing the dA ± plots. The dotted line across A–D shows the timing of peak flow used to measure acceleration time (AT), demonstrating it arises as a consequence of the arrival of the backwards compression wave overcoming the forward compression wave (arrow). Time = 0 corresponds to the onset of data acquisition as triggered by the R wave on cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) vectorcardiography.