Fig. 3.
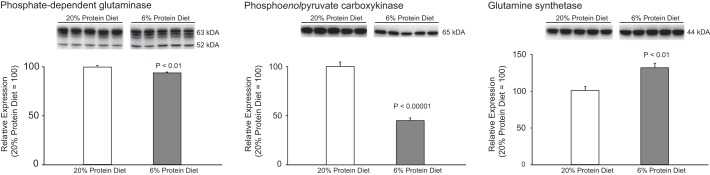
Effect of dietary protein restriction on proteins involved in ammoniagenesis. Left: renal cortical phosphate-dependent glutaminase (PDG) expression. Dietary protein restriction induced a small, but statistically significant, decrease in PDG expression. The multiple bands are due to kidney-specific endogenous proteinases (25). Middle: changes in renal cortical phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK) expression. Dietary protein restriction induced a substantial, statistically significant, decrease in PEPCK expression. Right: renal cortical glutamine synthetase expression. Glutamine synthetase catalyzes the regeneration of glutamine and decreases intrarenal ammonia availability. Dietary protein restriction resulted in a significant increase in glutamine synthetase expression as compared with 20% protein diet. The original blot for each of the proteins shown at right included tissues from mice with global Rhcg deletion provided either 20 or 6% protein diets and is shown in Fig. 8. Only the data from wild-type mice are shown at right. Values are means ± SE; n = 5/group.
