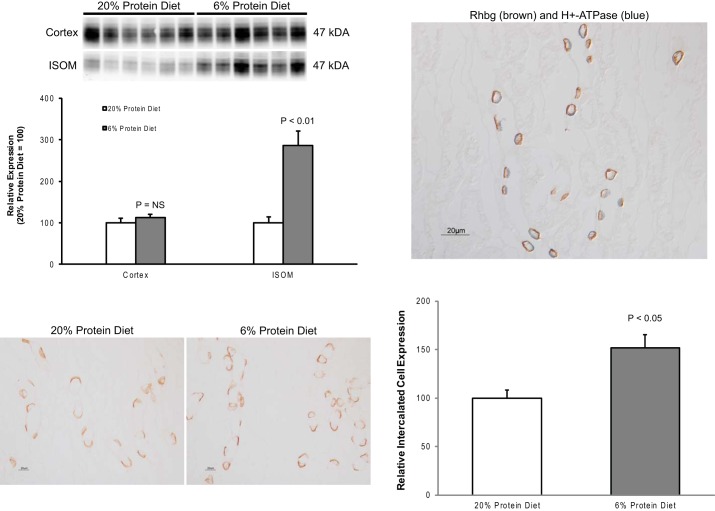
Fig. 5.
Effect of dietary protein restriction on Rhbg expression. Top left: effects of dietary protein restriction on steady-state Rhbg protein expression. There is no significant change in expression in the cortex, but dietary protein restriction induced a significant increase in expression in the outer medulla. Values are means ± SE; n = 6/group. Bottom left: immunolabel for Rhbg in the inner stripe of the outer medulla (ISOM) in control and low-protein diet-fed mice. Dietary protein restriction causes an increase in basolateral Rhbg immunolabel intensity in a subset of collecting duct cells. No expression is evident in noncollecting duct cells. Top right: colocalization of Rhbg (brown) with the intercalated cell marker H+-ATPase (blue) in the inner stripe of the outer medullary collecting duct. Rhbg expression in response to low-protein diet is restricted to cells identified as type A intercalated cells by the presence of apical H+-ATPase immunolabel. Bottom right: mean cellular Rhbg expression determined using quantitative immunohistochemistry. Dietary protein restriction resulted in a significant increase in mean Rhbg expression in the type A intercalated cell.