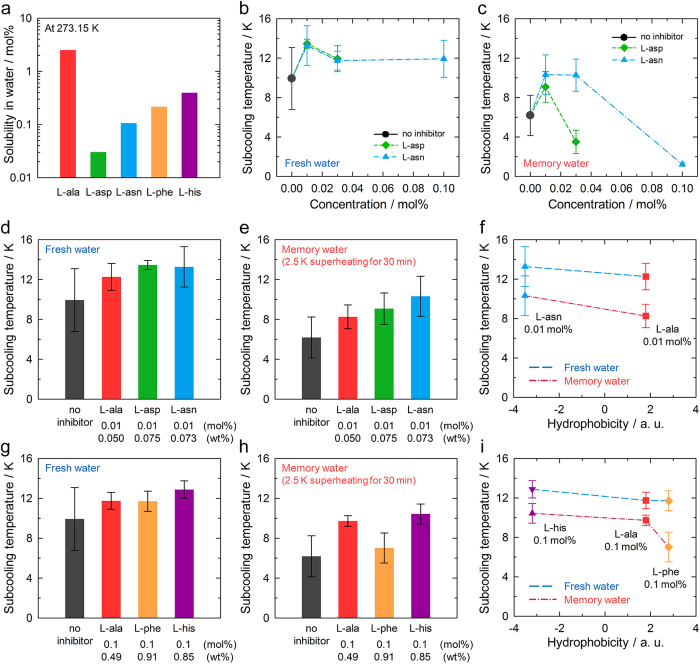
Figure 2. Heterogeneous nucleation kinetics of the CO2 hydrates.
(a) The solubilities of the amino acids in water at 273.15 K42,43. CO2 hydrate nucleation kinetics (b) in fresh water and (c) in memory water. Memory water was obtained from the dissociation of CO2 hydrate at a temperature 2.5 K above the phase equilibrium temperature for 30 min. The injection of KHIs at concentrations closed their solubilities led to failures in hydrate inhibition. CO2 hydrate nucleation kinetics in the presence of 0.01 mol% amino acids (d) in fresh water and (e) in memory water. (f) The correlation of subcooling temperatures at the onset of CO2 hydrate nucleation with the hydrophobicities. CO2 hydrate nucleation kinetics in the presence of 0.1 mol% amino acids (g) in fresh water and (h) in memory water. (i) The correlation of subcooling temperatures with the amino acid hydrophobicities. The values for the average and standard deviation are shown. L-phenylalanine had negligible influence on nucleation kinetics, especially in memory water, whereas all the other tested amino acids were found to be effective in inhibiting CO2 hydrate nucleation. The data for the system with no inhibitor or 0.1 mol% L-alanine were obtained from our previous report24.