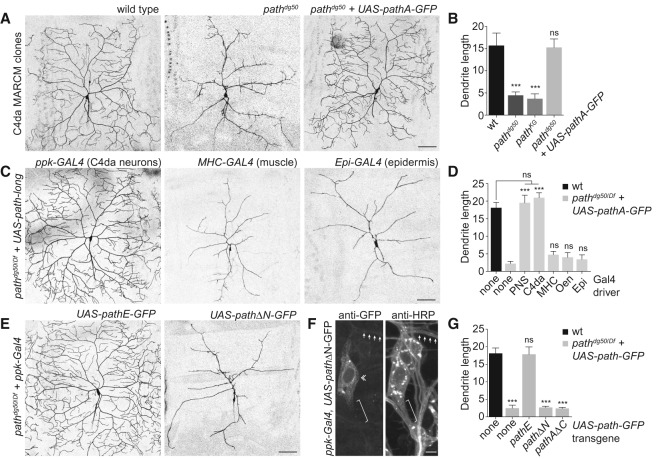
Figure 5.
path is required cell-autonomously for extreme dendrite growth. (A,B) path is required in neurons for dendrite growth. (A) Representative wild-type control, pathdg50, and pathdg50 + UAS-path-GFP ddaC C4da MARCM clones are shown. (B) Quantification of total dendrite length (in millimeters) for ddaC MARCM clones of the indicated genotypes. n ≧ 8 ddaC MARCM clones for each. (C,D) Neuronal path expression is sufficient for extreme dendrite growth. (C) The ability of UAS-path-GFP expression directed by a variety of Gal4 drivers to rescue dendrite growth defects of path mutants was assayed at 120 h AEL. C4da dendrites were visualized by a ppk-CD4-tdTomato reporter in control (UAS-path-GFP/+), path mutant (gal4/+; pathdg50/Df), or UAS-pathA-GFP-expressing path mutant larvae (gal4/UAS-path-A-GFP; pathdg50/Df). Representative images of rescue with the ppk-gal4, MHC-gal4, and A58-gal4 drivers are shown. (D) Quantification of rescue activity of Gal4 drivers at 120 h AEL. Gal4 drivers used to drive UAS-path-A-GFP in the larval body wall were as follows: (none) no Gal4 driver; (PNS [md neurons]) 21-7-Gal4; (C4da [C4da neurons]) ppk-Gal4; (MHC [muscle]) MHC-Gal4; (Oen [oenocytes]) OK72-Gal4; (Epi) A58-Gal4. n = 5 neurons for each genotype. (E–G) The N-terminal domain is required for Path function. (E) Representative images of C4da neurons from path mutant larvae expressing UAS-pathE-GFP (the short isoform of path) (left) or UAS-pathΔN-GFP (a version of path lacking the N-terminal intracellular domain) (right). (F) The N-terminal domain influences Path localization. Antibody staining shows distribution of PathΔN-GFP in C4da neurons (da neurons labeled by anti-HRP immunoreactivity). Arrows mark dendrites, a double chevron marks C4da soma, and a bracket marks the axon. (G) Quantification of rescue activity of neuronal expression of the indicated transgenes in path mutant larvae. n = 8 neurons for each genotype. Error bars represent standard deviation. (***) P < 0.001; (ns) not significant compared with wild-type controls, unless otherwise indicated in B and G, and compared with path mutants in D; one-way ANOVA with a post-hoc Dunnett's test. Bars: A–E, 50 μm; F, 10 μm.