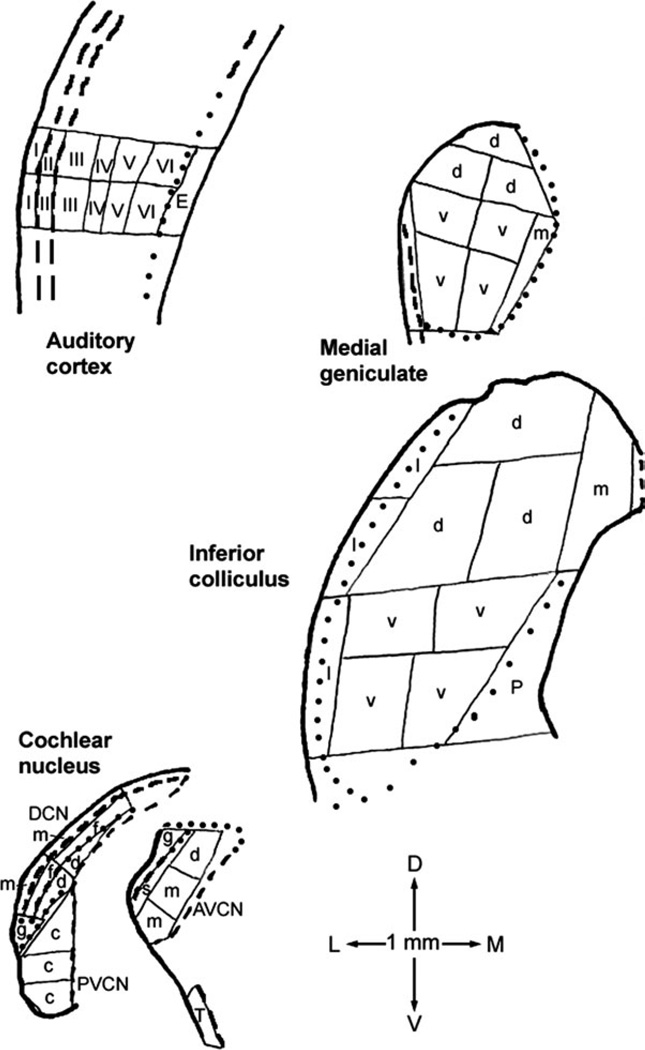
Fig. 1.
Examples of microdissection maps for coronal sections through the four major auditory regions sampled. A similar dissection strategy was used for all hamsters. The 1-mm scale at the bottom also shows dorsal (D), ventral (V), lateral (L), and medial (M) directions. Thin solid lines are cut-sample boundaries; thick solid lines are outside sectional boundaries; thick dashed lines are internal boundaries traced in the freeze-dried sections themselves; and dotted lines are internal boundaries traced from adjacent thionin-stained sections. Letters and numerals within samples identify those for which data were averaged for Tables I and II. Abbreviations are, for cochlear nucleus, AVCN, anteroventral cochlear nucleus, including dorsal (d), main (m), subgranular (s), and granular (g) regions; DCN, dorsal cochlear nucleus, including molecular (m), fusiform soma (f), and deep (d) layers; and PVCN, posteroventral cochlear nucleus, including caudal portion (c) and granular region (g); for inferior colliculus, dorsal (d), ventral (v), lateral (l), and medial (m) parts and periaqueductal gray (P); for medial geniculate, dorsal (d), ventral (v), and medial (m) parts; and for auditory cortex, layers I through VI and underlying external capsule (E). Compared with inferior colliculus subdivisions as defined for rats (Paxinos and Watson, 1998; Loftus et al., 2008), our most dorsal ‘‘d’’ sample, medial ‘‘d’’ sample of the second row, and ‘‘m’’ sample collectively approximate its dorsal cortex; the ventral part plus the lateral ‘‘d’’ sample of the second row its central nucleus; and the lateral part its lateral, or external, cortex. The dorsal, ventral, and medial parts of the medial geniculate as defined here approximately correspond to the same-named regions as defined for rats (Paxinos and Watson, 1998; Winer et al., 1999). The most lateral, unlabeled sample location in the medial geniculate map included some optic tract and some marginal zone of the medial geniculate (Paxinos and Watson, 1998; Morin and Wood, 2001).