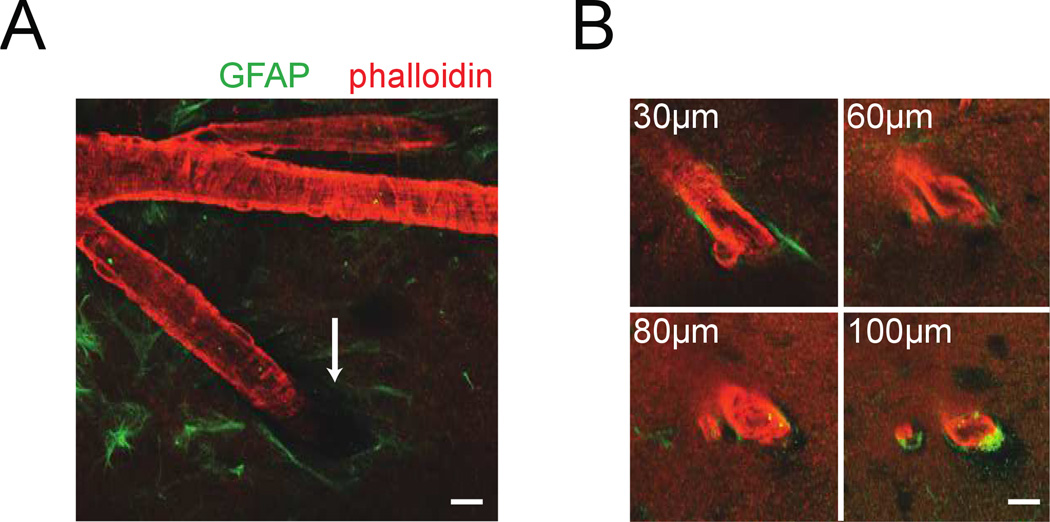
Figure 5. Visualizing arterioles and their interaction with the surrounding brain tissue.
A) 2PLSM image of a penetrating arteriole (red, actin labeled with rhodamine-conjugated phalloidin) and surrounding astrocytes (green, labeled with anti-GFAP antibody) in an ex vivo brain. The pial funnel, a hole in the brain into which the penetrating vessel enters, is marked with the white arrow. B) Four images of the penetrating arteriole in A taken at increasing depths below the pia. The perivascular space between astrocytes and vessel wall below the surface was very small. Any dilation of the intracortical vessel would compress the surrounding brain tissue. Scale bars 20µm.