Fig. 3.
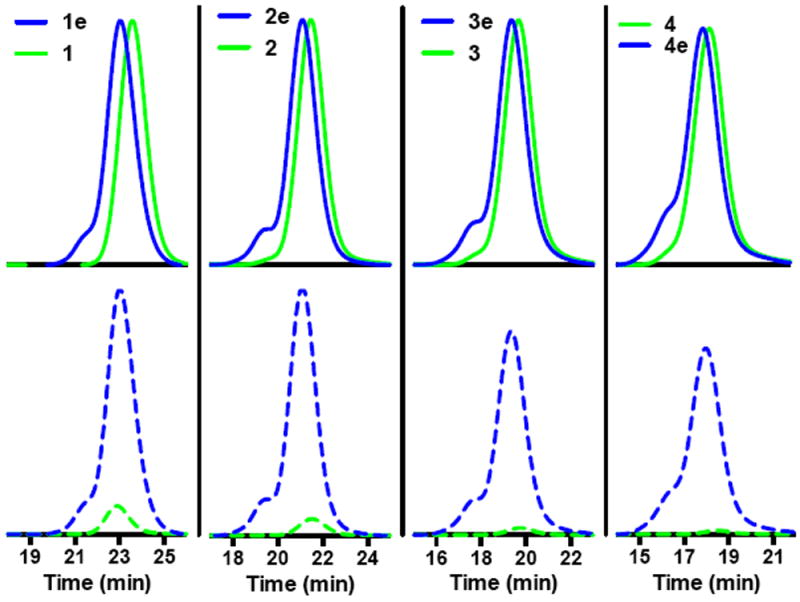
GPC chromatograms showing conjugation of ECT to polymeric scaffolds with different molecular weights. Poly(DMAcoHEAm) before (green traces) and after CTA (blues traces) conjugation was analyzed via GPC at a constant injection volume of 0.5 mg/mL. (top) Overlay of the RI response which is proportional to the injected mass. (bottom) Overlay of the UV response at 310 nm where thiocarbonyl thio groups show strong absorbance. Molecular weight, Đ, and number of ECT functional groups per polymer are as follows: (1) 15 500/1.03/1 (1e, graft) 19 590 Da/1.05/10 (2) 35 600 Da/1.03/1 (2e, graft) 44 800 Da/1.09/20 (3) 69 800 Da/1.04/1 (3e, graft) 86 400/1.11/36 (4) 116 500/60/1.06 (4e, graft) 147 800/1.14/60. Absolute molecular weights and Đ values where determined via SEC in DMF eluent. The extinction coefficient of ECT in DMF at 310 nm (9422 L/mol) was used to determine the concentration of polymer conjugated RAFT agent. The number of ECT functional groups per polymer was then determined by comparing these values to the respective absolute molecular weights determined by SEC.
