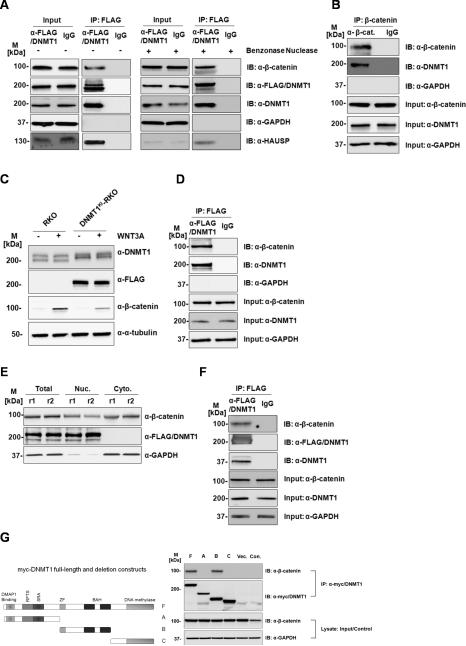
Figure 1. Dnmt1 protein interacts with β-catenin in colorectal cancer cells.
(A) DNMT1 (FLAG) immunoprecipitates β-catenin in HCT116 cells. Total protein lysate from HCT116 with Benzonase untreated (-) or treated (+) was used in the immunoprecipitation and elution fractions were loaded on gel and blotted (B) β-catenin immunoprecipitates DNMT1 in HCT116 cells (C) β-catenin is induced by Wnt3a stimulation in both RKO and DNMT1KI-RKO cells. (D) Dnmt1 (anti-FLAG) immunoprecipitates β-catenin in DNMT1KI-RKO cells. (E) Sub-cellular fractionation and protein expression levels inDNMT1KI-HCT116 cells. (F) Dnmt1 (anti-FLAG) immunoprecipitates β-catenin in nuclear fraction of DNMT1KI-HCT116 cells. Twenty micrograms of proteins from each fraction was loaded on SDS-PAGE followed by Western blot analyses with anti-Dnmt1, anti-FLAG, anti-β-catenin, anti-HAUSP, anti-α-tubulin, and anti-GAPDH. (M - standard protein marker; r - biological replicate; Nuc - nuclear fractions; Cyto - cytoplasmic fractions; IP – immunoprecipitation; IB – immunoblotting; Input indicates equal loading for IP experiments). (G) The central portion of Dnmt1 interacts with β-catenin. HEK293 cells were transfected with plasmids expressing full length Myc-tagged Dnmt1 (F), three Myc-tagged Dnmt1 deletion constructs (A, B, C) as shown in the diagram of Dnmt1 protein as well as empty plasmid vector (Vec.). Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-Myc antibodies and cell lysate from non-transfected HEK293 cells (Con.) were used as immunoprecipitation control. Elution fractions were then loaded on SDS-PAGE followed by Western blot analyses with anti-β-catenin antibodies. M refers to standard protein marker