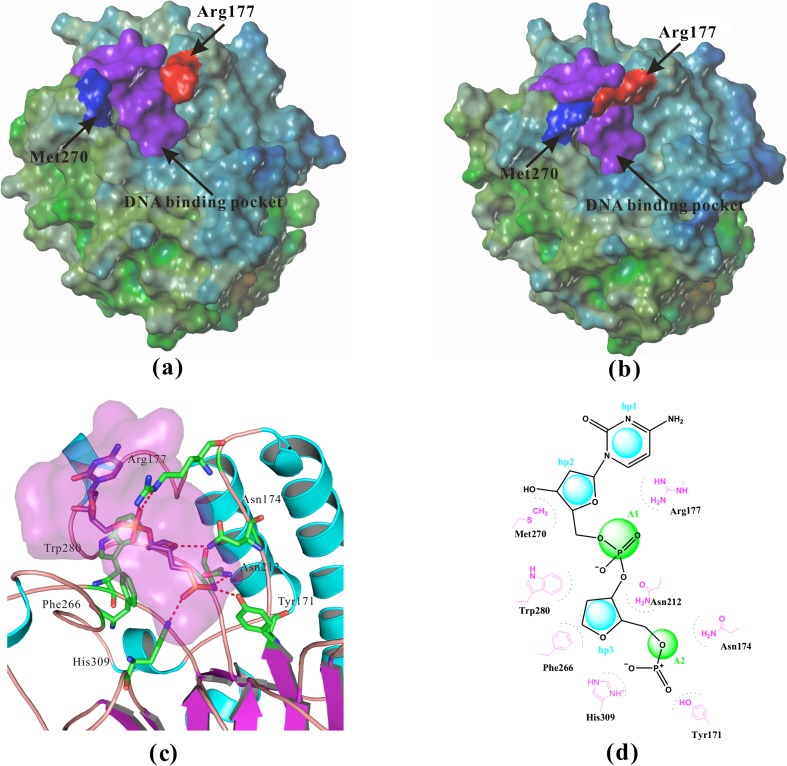
Fig. 1.
Structural details of APE-1. a The surface of crystal structure of apo-APE-1 (PDB/1BIX) [31], Arg177 was far away from Met270, so the potential binding pocket was open. b The surface of crystal structure of APE-1 bound with DNA (PDB/1DEW) [32], Arg177 and Met270 covered the potential binding pocket. c The interactions between APE-1 and abasic site fragment in the crystal structure of APE-1 bound with DNA (PDB/1DEW), several important residues including Tyr171, Asn174, Asn212, and His309 form strong ionic or H-bonding interactions with the negatively charged 5'-phosphate, a hydrophobic pocket surrounded by residues Phe266, Met270, Trp280, and Leu282. d Two-dimensional pharmacophore model hp3A2 with three hydrophobic or hydrophobic aromatic centers (hp) and two H-bond acceptors (A) was generated to represent APE-1 interactions with abasic DNA (PDB/1DEW). Distance restrictions of this pharmacophore model were listed in Table 1