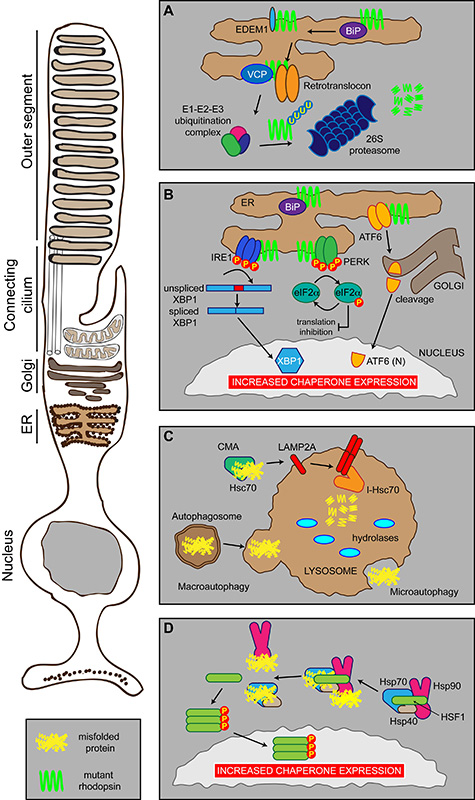
Figure 2. Photoreceptor proteostasis networks.
Schematic showing the proteostasis networks in a rod photoreceptor that deal with misfolded proteins, such as P23H rod opsin (mutant rhodopsin in green), or cell stress. (A) ERAD. Misfolded proteins are detected by the ER quality control machinery (including BiP, EDEM1, VCP) and shuttled to the cytoplasm by the retrotranslocon where they are ubiquitylated before being degraded by the proteasome. (B) The UPR. Misfolded proteins, such as mutant rod opsin, in the ER are recognised by three sensors: IRE1, PERK and ATF6 that inhibit protein synthesis and stimulate the production of chaperones and the ERAD machinery (see text for details). (C) Autophagy. Misfolded proteins can be degraded by three modes of autophagy: macroautophagy, microautophagy or CMA. (D) The HSR. Molecular chaperones Hsp70, Hsp40 and Hsp90 can exist in a complex in the cytosol with their transcription factor HSF1. Upon binding misfolded proteins, Hsp70, Hsp40 and Hsp90 dissociate from HSF1, which can trimerise and activate via phosphorylation. This results in traffic to the nucleus leading to increased chaperone expression.