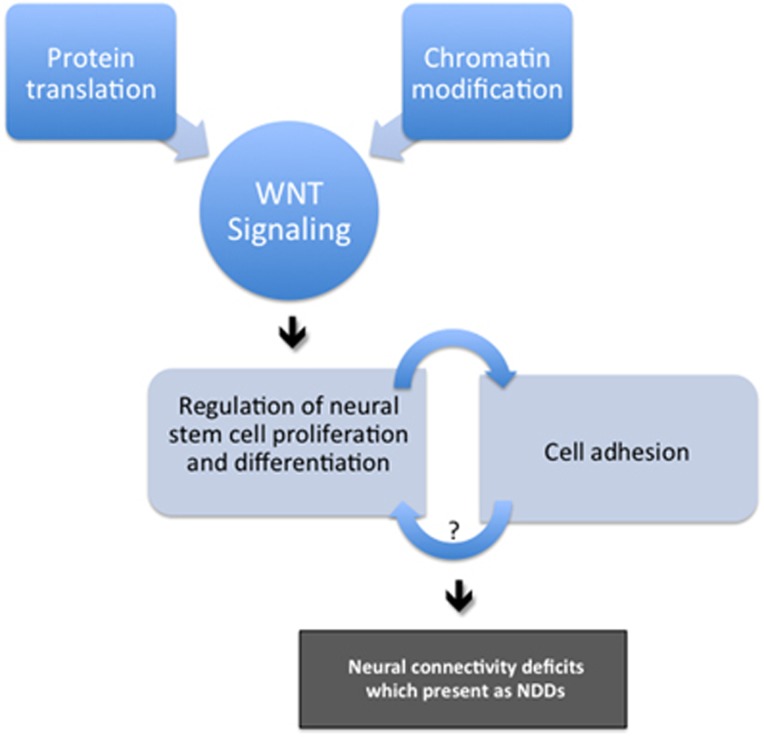
Figure 4.
Molecular model for neurodevelopmental disorders. Genes with mutations associated with NDDs might affect specific cell processes such as protein translation or chromatin modification in such a way as to impact pathways important in NSC proliferation or differentiation, such as the WNT signaling pathway. The measureable outcome of different genetic variation associated with NDDs may be NSCs with altered regulation of the balance between NSC proliferation and differentiation. These vulnerabilities, specific to each mutation associated with NDDs, might affect the timing of neural stem cell differentiation causing neurons to connect inappropriately in a neural circuit or respond uncharacteristically to attractant or repellent cues. NDD, neurodevelopmental disorder; NSC, neural stem cell.