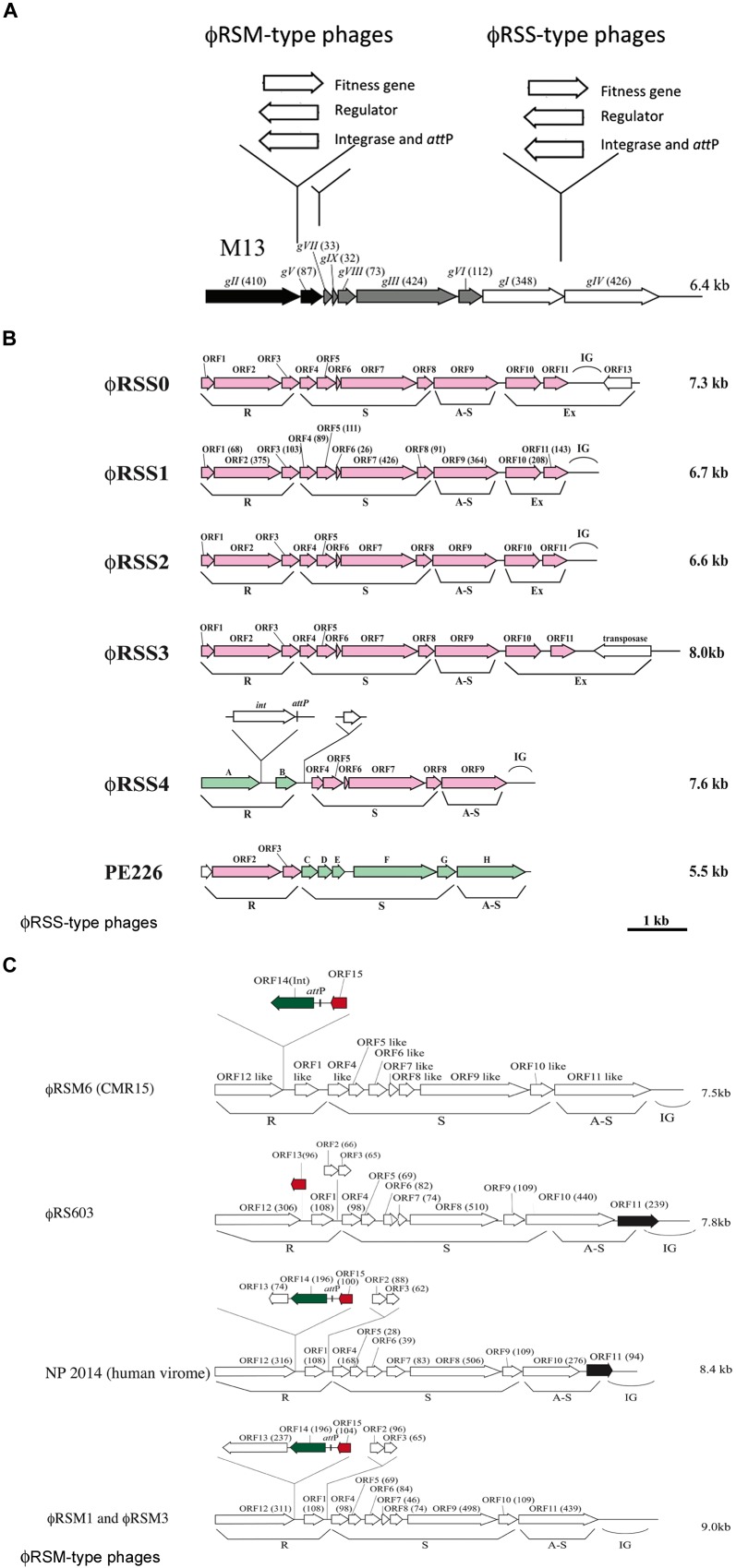
FIGURE 1.
Diversity of genomic arrangement in filamentous phages of Ralstonia solanacearum. (A) For ϕRSM-type and ϕRSS-type phages, gene insertion sites are shown along the linear genomic map of Escherichia coli phage M13 (Model and Russel, 1988; Marvin, 1998). Arrows indicate the direction of transcription and represent open reading frames (ORFs) or genes. The functional modules for replication (R), structure (S), and assembly and secretion (A-S) are indicated according to the M13 model. ORF sizes (in amino acids) are in parentheses. IG, intergenic region. (B) Genomic organization of ϕRSS-type phages. According to the E. coli M13-model, ORFs identified in the phage genome are grouped into the R, S, and AS functional modules. IG, large intergenic region. ϕRSS0, ϕRSS2, ϕRSS3, and ϕRSS4 were derived from prophages of strains C319, M4S, MAFF106611, and MAFF211271, respectively. PE226 is a phage of Korean strains of R. solanacearum (Murugaiyan et al., 2010). ORFs shown in pink are homologous to ϕRSS1 ORFs, and those in green are homologous to ϕRSM-type ORFs. (C) Genomic organization of ϕRSM-type phages. ϕRSM1 and ϕRS603 were isolated from soil (Kawasaki et al., 2007; Bich Van et al., 2014). ϕRSM3 and ϕRSM6 are prophages of strains MAFF730139 and CMR15 (phylotype III, Remenant et al., 2010), respectively. NP204 is similar to a phage found in the human virome (Ralstonia phage 1 NP2014, accession no. AHI87735.1). ORFs shown in green, red, and black are genes encoding an integrase (Int), transcriptional repressor, and ϕRSS1-ORF11-like ORF, respectively.