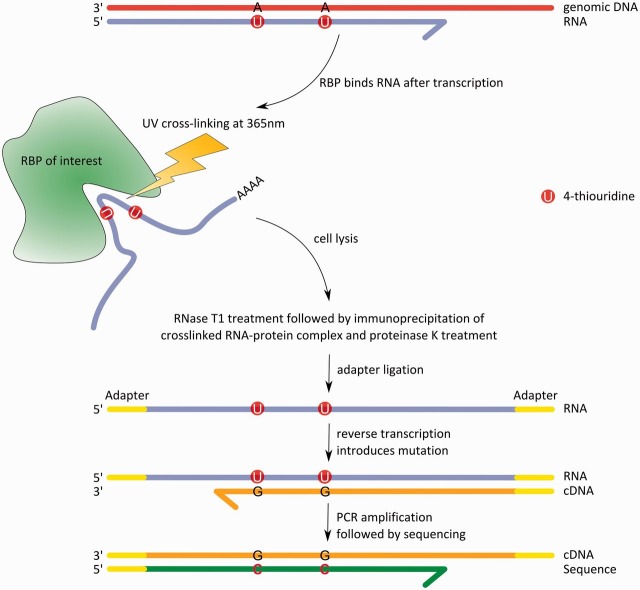
Figure 2:
Process from the RNA–RBP interaction to the RNA sequence using PAR-CLIP. First, the mRNA with incorporated 4-thiouridines is bound within the binding pocket of the RBP. Next, the cell is irradiated with UV light at 365 nm, thereby cross-linking single nucleotides from the RNA to amino acids of the RBP. The RNA–protein complex is then extracted by cell lysis, and the mRNA portion that is not protected by the binding pocket is cleaved by RNase T1. Afterward, immunoprecipitation and proteinase K are used to extract and then separate RNA and RBP. Adapters are ligated to the 3′ and 5′ ends of the free mRNA to make the short RNA fragments accessible for reverse transcription, when conversions occur. These conversions can be seen as T–C mutations on the sequence level (adapted from [39]).