Figure 1.
Identification of Kcnn4 within a Genetically Regulated Macrophage Multinucleation Network
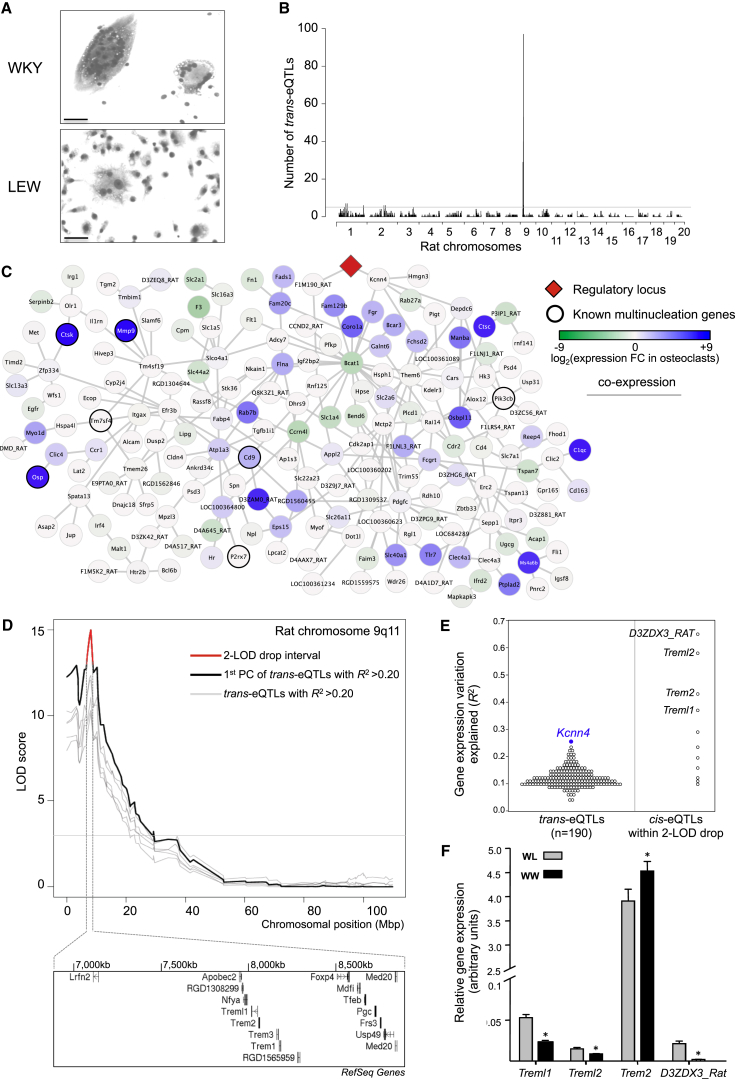
(A) Genetic determinants of macrophage multinucleation were explored in WKY and LEW bone-marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs). WKY macrophages fuse spontaneously to form multinucleate giant cells (MGCs) in vitro and show a marked phenotypic difference when compared to LEW macrophages, which form very few MGCs at day 6 of cell differentiation (original bars, 50 μm).
(B) eQTL analysis of the backcross (BC) BMDMs identifies a unique master regulatory locus on rat chromosome 9q11. Genome-wide distribution of trans-eQTLs shows a single locus regulating the expression of 190 transcripts in trans, suggesting master regulation of the trans-eQTL cluster. The detailed eQTL hot spots with the corresponding SNP positions are reported in Table 1.
(C) Gene coexpression network of the 190 trans-eQTLs is enriched for osteoclast-expressed genes where the master regulatory locus is highlighted in red. Each gene in the network is represented as a circle (node), and the fold change in expression refers to overexpression (blue) or underexpression (green) in osteoclasts as compared to average expression in other cell types (Supplemental Experimental Procedures). Known multinucleation genes (Mmp9, Ctsk, P2rx7, etc.) are indicated with thick circles. The edges represent coexpression between the two transcripts as identified by ARACNE (Margolin et al., 2006).
(D) Genetic linkage showing the principal component of all the trans-cluster transcripts (LOD > 10) together with trans eQTLs with variation in gene expression explained by the SNP (R2) >0.2. The 2-LOD drop interval (in red) and the underlying positional candidates within 2 Mb are also shown. The annotated gene names are according to RefSeq.
(E) The cis-eQTLs within the 2-LOD drop interval (in red) are shown together with the trans cluster. Treml1, Trem2, D3ZDX3_Rat, Treml2 are positional candidates (R2 > 0.25) and among the trans-eQTLs, Kcnn4 (in blue) is the most significant trans-eQTL.
(F) Quantitative real-time PCR analysis on the positional candidates in BC BMDMs according to their genotype (WKY homozygous, WW; WKY/LEW heterozygous, WL). Note that the expression levels of Trem2 are increased at least 90-fold when compared to other positional candidates.
Error bars indicate SEM, ∗p < 0.01. See also Figures S1 and S2.