Figure 6.
Kcnn4 Regulates Ca2+-NFATc1 Signaling in Multinucleate Macrophages
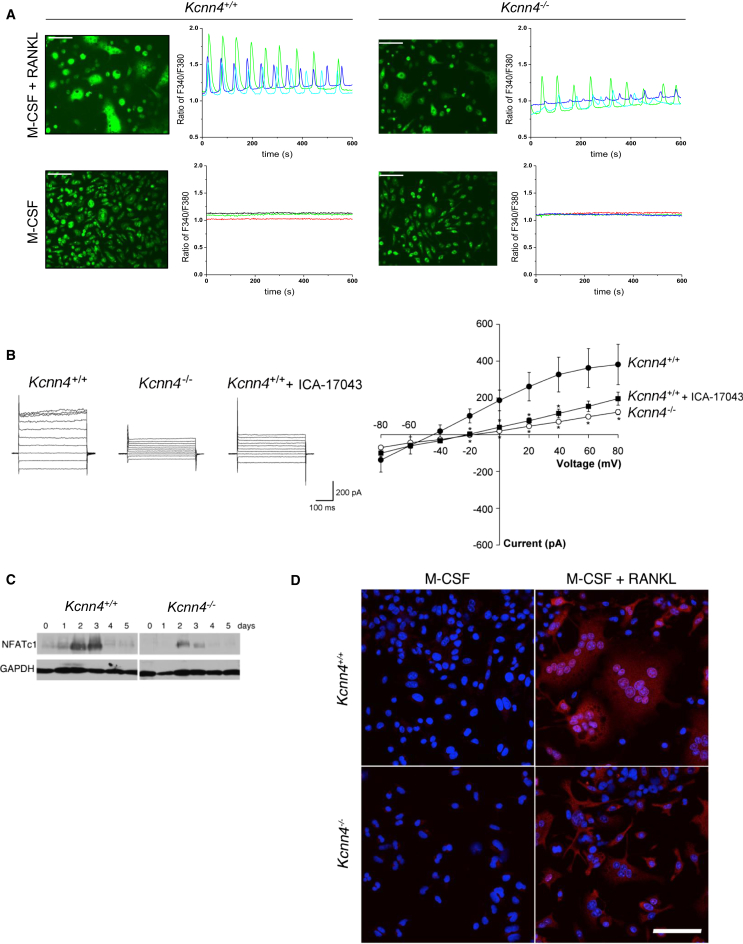
(A) Ca2+ oscillations were recorded by intracellular Ca2+ imaging using fura-2 in multinucleate osteoclasts from Kcnn4+/+ and Kcnn4−/− mice. Fluorescence images of cells is shown on the left panel, whereas traces of change in fura-2 fluorescence ratio in single cells treated with M-CSF only or M-CSF and RANKL for 72 hr are shown on the right panel. Note the decrease in Ca2+ oscillations associated with Kcnn4 deficiency, and the absence of Ca2+ oscillations in the presence of M-CSF alone, independent of Kcnn4. These experiments were repeated multiple times with similar results, and one representative result is shown. Original bars, 50 μm.
(B) Representative current responses to increasing voltage steps (−100 mV to +80 mV; 400 ms) observed in mouse BMDMs from Kcnn4+/+ and Kcnn4−/− mice treated with M-CSF (25 ng/ml) and RANKL (40 ng/ml) for 5 days (left panel). I–V plot demonstrates the average current/voltage relationship observed (right panel). Data points for Kcnn4−/− and Kcnn4+/+ macrophages treated with the Kcnn4 inhibitor ICA-17043 (1 μM) were statistically different from Kcnn4+/+ in the range of −20 mV to +80 mV (mean ± SD, ∗p < 0.05; n = 10), with the exception of Kcnn4+/+ + ICA-17043 at + 60 mV (mean ± SD, p = 0.06; n = 10) and +80 (mean ± SD, p = 0.11; n = 10). There was no significant difference between Kcnn4−/− macrophages and Kcnn4+/+ treated with ICA-17043.
(C) NFATc1 protein levels in BMDMs from Kcnn4+/+ and Kcnn4−/− mice. BMDMs isolated from Kcnn4+/+ and Kcnn4−/− mice were cultured in the presence of M-CSF (25 ng/ml) and RANKL (40 ng/ml) and subjected to western blot analysis at the indicated times using antibodies directed against NFATc1. GAPDH served as an internal control for equal loading of proteins on a SDS-PAGE protein gel. Note the lower abundance of NFATc1 in Kcnn4−/− macrophages compared with Kcnn4+/+ cells. This figure is representative of several experiments performed with similar results.
(D) BMDMs isolated from Kcnn4−/− and Kcnn4+/+ mice were treated with M-CSF (25 ng/ml) alone or supplemented with RANKL (40 ng/ml) for 5 days and subjected to immunocytochemistry using anti-NFATc1 antibody. Note the decrease in immunoreactive NFATc1 in the nuclei of Kcnn4−/− macrophages treated with RANKL compared with Kcnn4+/+ cells.
Original bars, 100 μm. See also Figure S6.