Figure 3.
Alternative Spliced Forms of Genes Specific to Each Stage of Reprogramming
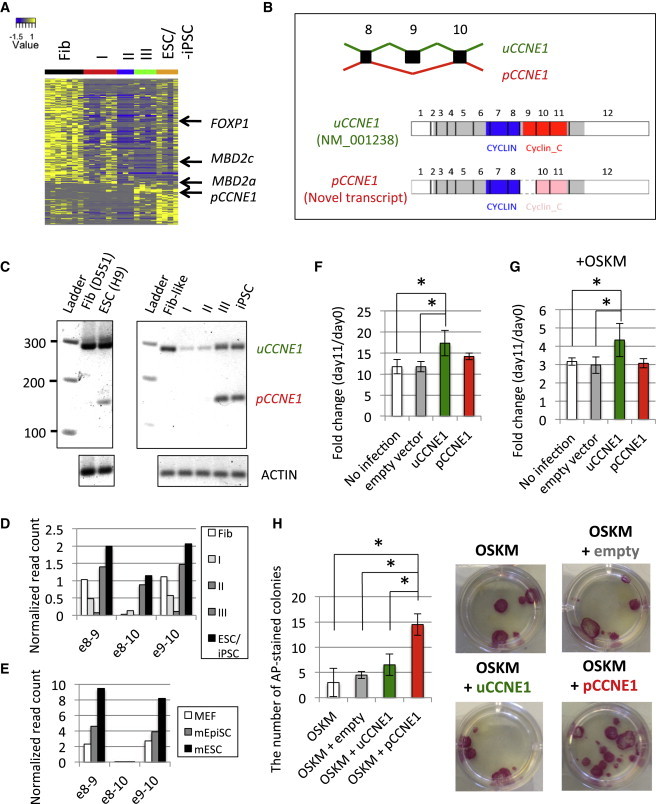
(A) Differential expression patterns of splice junctions. Colors represent the normalized read count mapped to each splice junction.
(B) Schematic representation of functional domains of splicing isoforms of CCNE1. Gray, blue, and red rectangles represent open reading frame, CYCLIN, and Cyclin_C domain, respectively. Pink rectangles represent the truncated Cyclin_C domain resulting from exon 9 skipping.
(C) RT-PCR assay using primers targeting exons 8 and 10. (Left) is derived from parental fibroblasts and H9 ESCs. (Right) is derived from sorted intermediate populations: Fib-like (w1 CD13+ GFP+), type I (w2 CD13+ GFP+ SSEA4+), II (w4 GFP+ SSEA4+ TRA160+), III (w4 GFP− SSEA4+ TRA160+), and iPSC.
(D and E) Exon 9 skipping of CCNE1 in (D) human and (E) mouse somatic and pluripotent stem cells.
(F and G) Effect of CCNE1 variants on cell growth rate. Fold change of cell count at day 11 to that at day 0 was calculated (F) without and (G) with OSKM induction (∗p < 0.05 by one-side t test, three biological replicates). Error bars represent SD.
(H) Positive regulation of hiPSC reprogramming by pCCNE1 overexpression. (Right) represents representative AP+ colonies in 12-well plate induced by overexpression of empty vector, uCCNE1, or pCCNE1 with reprogramming factors OSKM (three biological replicates). Error bars represent SD.
See also Figures S2 and S3.
