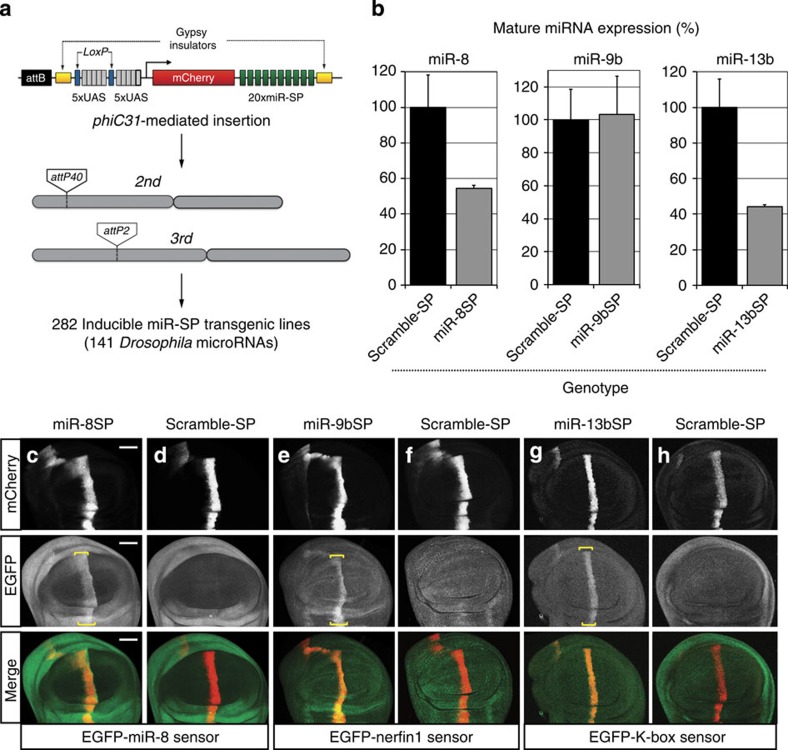
Figure 1. A transgenic library of conditional miRNA competitive inhibitors.
(a) Second-generation SP elements consist of 20 miRNA binding sites with mismatches at positions 9–12 placed in the 3′-untranslated region of mCherry under the control of 10 tunable Gal4 UAS binding sites. The entire cassette was cloned in an attB vector containing gypsy insulators. phiC31-mediated positional integration was used to generate a library of 282 inducible lines covering 141 high-confidence Drosophila miRNAs, at defined landing sites on the second (attP40) and third (attP2) autosomes. (b) Quantification of endogenous miR-8, miR-9b and miR-13b mature miRNA levels using Taqman quantitative PCR in third instar larvae following ubiquitous expression (tubulin-Gal4) of corresponding miR-SP constructs compared with Scramble controls (Student's t-test: 13b, P=0.02; error bars, s.e.m., n=3 biological replicates with 10 animals per sample). (c–h) Targeted expression of miR-8SP (c; scale bars, 50 μm), miR-9bSP (e) and miR-13bSP (g) with ptc-Gal4 in wing imaginal discs ubiquitously expressing tubulinEGFP-miR-8, tubulinEGFP-nerfin1 and tubulinEGFP-K-box sensors respectively. Tissue-specific upregulation of sensor levels was observed in cells along the anterior–posterior boundary of the disc. No change was apparent following expression of a Scramble-SP control (d,f,h).