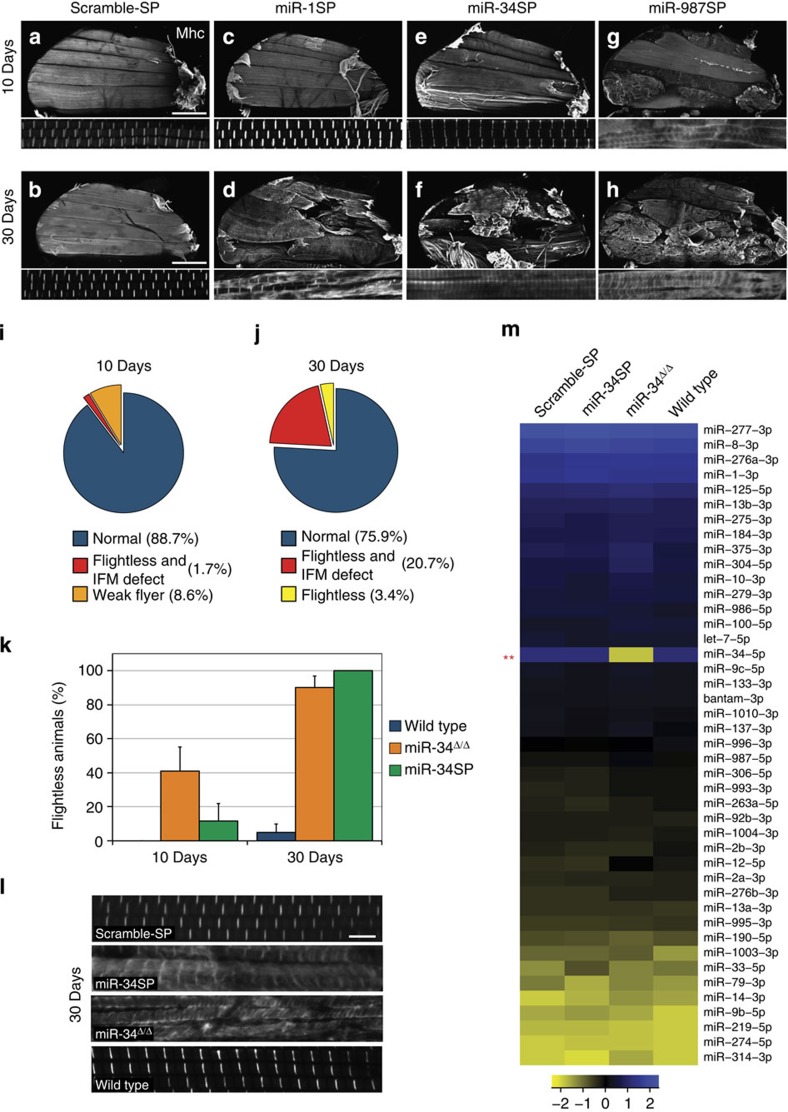
Figure 4. Twelve miRNAs are required to maintain flight muscle structure.
Fifty-eight lines were assayed for flight at 10 and 30 days post eclosion, and all lines that displayed significant flight deficits were then assayed for IFM morphology (a–h). Sagittal bisections of the adult thorax stained for actin and myosin heavy chain (Mhc) shown at low (top panel) and high magnification (bottom panel). Normal IFM and sarcomere morphology in 10- and 30-day-old Scramble-SP controls (a,b; scale bars, 200 μm), late-onset IFM phenotype following miR-1SP expression (c,d) or miR-34SP expression (e,f), and early-onset IFM defects in miR-987SP animals (g,h). A summary of the lines that display flight and IFM phenotypes at 10 days post eclosion (i) is shown for comparison with the 30-day results shown in j; red represents all SP lines that display both flight and IFM defects, whereas orange and yellow represent animals with no detectable IFM morphology defect that were flight impaired or flightless, respectively. (k–l) Comparison of miR-34SP and miR-34Δ/Δ null mutants. Null mutant adults (orange bars) display a stronger flightless phenotype at 10 days but are comparable to miR-34SP (green bars) at 30 days (k); error bars, s.e.m., n=3 replicates of 20 animals. IFM sarcomere morphology and Mhc distribution and pattern are comparable in miR-34SP and miR-34Δ/Δ null mutants at 30 days (displaying 15.7% penetrance (n=19), compared with 25% in miR-34SP; l; scale bar,5 μm). (m) NanoString nCounter profiling of adult thoracic muscle. All miRNAs expressed above background values are represented. Only the levels of mature miR-34–5p were substantially reduced in the null mutant. Statistical significance was established in this case by comparing the expression values of miR-34Δ/Δ to the wild-type control using the NanoStringNorm package in R (t-test, **P<0.003). For all other genotypes, statistical significance was established by comparing the miR-SP values, against miR-34Δ/Δ, Scramble-SP and wild-type controls. No other endogenous miRNA levels change significantly in miR-34SP or miR-34Δ/Δ animals compared with Scramble-SP or wild-type controls (see Methods section).