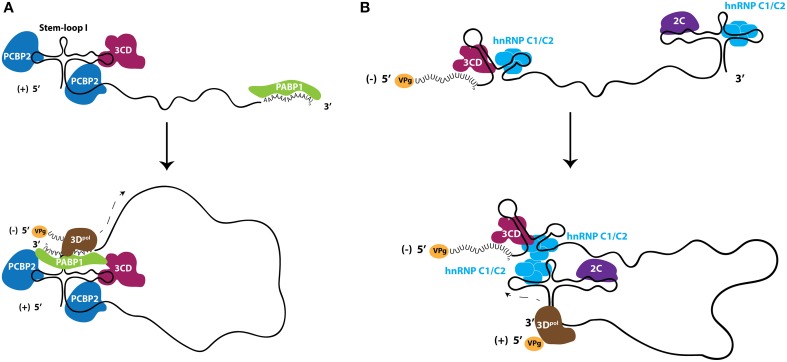
Figure 4.
Ribonucleoproteins (RNPs) comprised of nuclear-resident proteins facilitate enterovirus RNA replication. (A) Nuclear-resident proteins PCBP2 (dark blue) and PABP1 (green) act in conjunction with viral protein 3CD (fuchsia) to circularize genomic RNA for use as templates to produce negative-sense RNA intermediates. (B) Nuclear protein hnRNP C1/C2 (light blue) interacts with both termini of negative-sense RNA molecules and is hypothesized to circularize the negative-sense template to promote genomic RNA production. Although likely in the form of double-stranded RNA, the negative-sense RNA is shown here as single stranded for clarity. Viral protein 2C (purple) interacts with the 5′-terminus of negative-sense RNA, although the direct function of this protein in viral RNA replication is unclear. The viral RNA-dependent RNA polymerase 3Dpol (brown) is recruited to these circularized templates and initiates viral RNA synthesis. VPg (yellow), the viral protein that primes RNA synthesis, is found on RNA molecules that have not been translated.