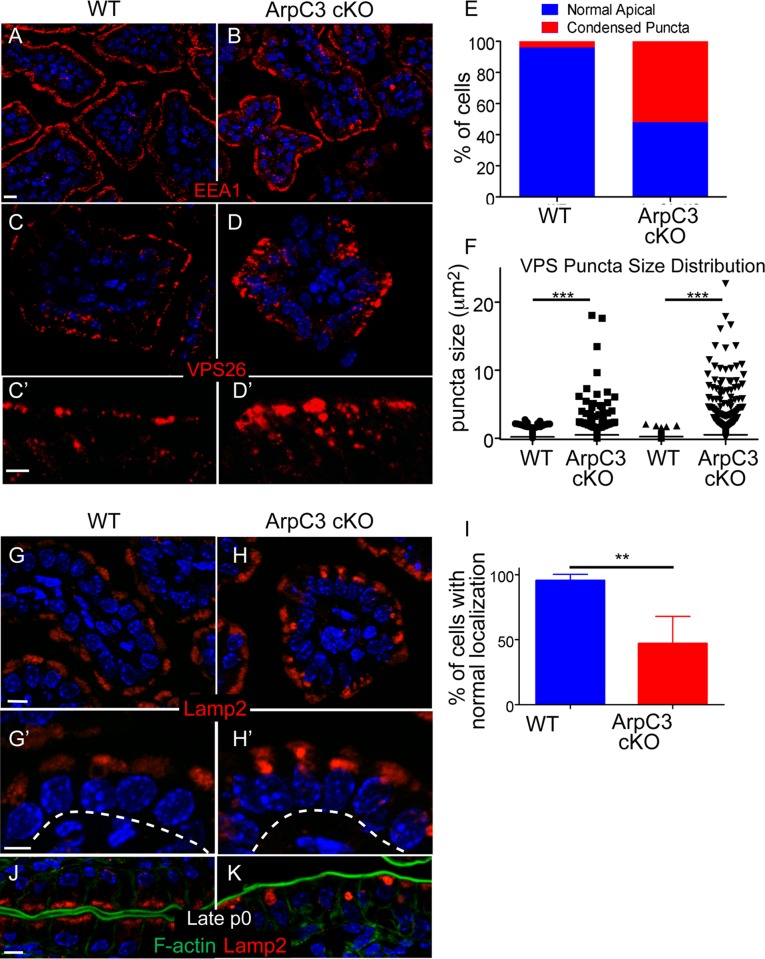
FIGURE 3:
Defects in retromer and lysosomal pools in ArpC3 cKO intestines. WT and ArpC3 cKO intestines were stained with antibodies against the early endosomal marker EEA1 (red) (A,B) or with antibodies against the retromer subunit VPS26 (red) (C–D′). (C′, D′) Magnified views of the apical regions of the intestine. (E) Quantitation of the number of enterocytes with normal/abnormal VPS26 localization. Intestines from WT and mutant animals from two different litters were used for analysis; p = 0.004. (F) Quantitation of the size of VPS26 puncta from two distinct WT and ArpC3 cKO intestines. p = 0.007. (G–H′) Staining for the lysosomal protein Lamp2 (red) in WT and ArpC3 cKO intestinal sections. (G′, H′) Higher-magnification views of the apical localization. Dashed lines indicate basement membranes. (I) Quantitation of cells with normal Lamp2 localization in WT and ArpC3 cKO intestines. Two mice for each genotype; p < 0.01. (J, K) Localization of Lamp2 (red) and F-actin (green) in intestines from neonates taken at late P0. Scale bars, 10 μm, except C′, D′, G′, and H′, 5 μm.