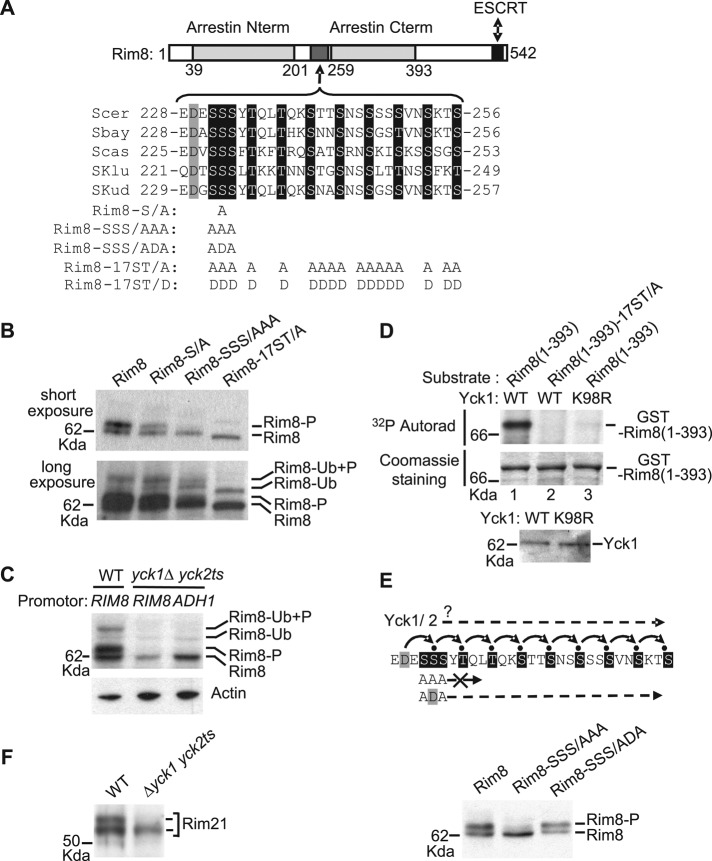
FIGURE 4:
Casein kinase 1–mediated phosphorylation of Rim8 interdomain connector (hinge). (A) Conservation of a cluster of Ser/Thr residues in the hinge region of Rim8 orthologues in the Saccharomyces clade. Top, schematic representation (to scale) of Rim8, showing the positions of the arrestin N-terminal and C-terminal PFAM domains, the ESCRT binding region, and the Ser/Thr cluster. The alignment (ClustalW) shows the conserved Asp (gray shading) and Ser/Thr (black shading) residues in S. cerevisiae (Scer), Saccharomyces bayanus (Sbar), Saccharomyces castellii (Scas), Saccharomyces kluyveri (Sklu), and Saccharomyces kudriavzevii (Skud). The position and amino acid substitutions for each Rim8 mutant are shown below. (B) Phosphorylation of Rim8 hinge region. Y04414 (rim8∆) was transformed with pHA-Rim8 or the mutant derivatives pHA-Rim8-S/A, pHA-Rim8-SSS/AAA, and pHA-Rim8-17ST/A. After a shift to pH 7.5, protein extracts were prepared by glass bead disruption, immunoblotted with anti-HA, and visualized after short (top) or long (bottom) autoradiography exposure to detect ubiquitinated species. Position of phosphorylated (P) and/or ubiquitinated (Ub) Rim8 is indicated. Note that the Rim8-17ST/A mutant migrates with slightly higher mobility than wild- type Rim8. (C) Casein kinase 1–dependent phosphorylation of Rim8. LRB341 (WT) and LRB362 (yck1∆ yck2ts) were transformed with pHA-Rim8 or pADH1-HA-Rim8, expressing HA-Rim8 under its own promoter or ADH1 promoter, respectively. Transformants were grown at a semipermissive temperature for yck2ts (30ºC). After a shift to pH 7.5, protein extracts were prepared by glass bead disruption and immunoblotted with anti-HA (top) or anti-actin (bottom) antibodies. (D) In vitro phosphorylation of Rim8 hinge region by casein kinase 1. Top, in vitro phosphorylation assay of GST-Rim8(1-393), or the corresponding mutant derivative GST-Rim8(1-393)-17ST/A, by affinity-purified His-tagged Yck1 or inactive Yck1-K98R. The 32P incorporation and protein levels were determined by autoradiography (top) and Coomassie staining (bottom), respectively. Bottom, immunoblot analysis of purified His-tagged Yck1 and Yck1-K98R with anti-His antibody (10% of the reaction). (E) Sequential phosphorylation of Rim8. Top, model for the cascade of CK1-mediated phosphorylations of Rim8. Small black circles represent phosphate groups. Bottom, Y04414 (rim8∆) was transformed with pHA-Rim8 or the mutant derivatives pHA-Rim8-SSS/AAA and pHA-Rim8-SSS/ADA. Protein extracts were prepared by glass bead disruption and immunoblotted with anti-HA antibody. (F) Same assay as in C with Rim21. LRB341 (WT) and LRB362 (yck1∆ yck2ts) were transformed with pRim21-HA, and protein extracts were immunoblotted with anti-HA antibody.