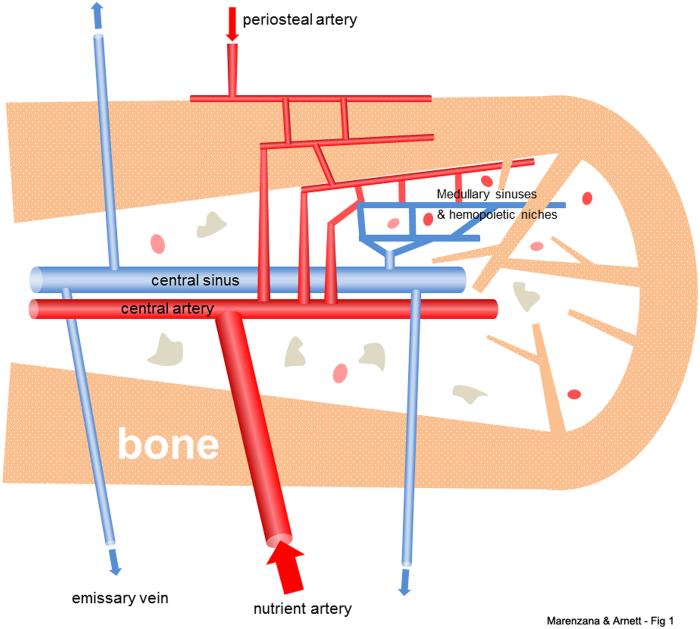
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram showing general arrangement of the vascular supply to healthy adult bone. The main blood supply is derived from one or more nutrient arteries, which penetrate to the medulla and connect to the smaller periosteal arterial supply to enable perfusion of cortical bone. The arterial branches drain into arterio-venous sinuses in the medulla that support hematopoietic and stromal cells. Blood exits the medullary cavity via multiple small veins that penetrate the cortex. Thus, perfusion is predominantly centrifugal, at least in young adult bone.