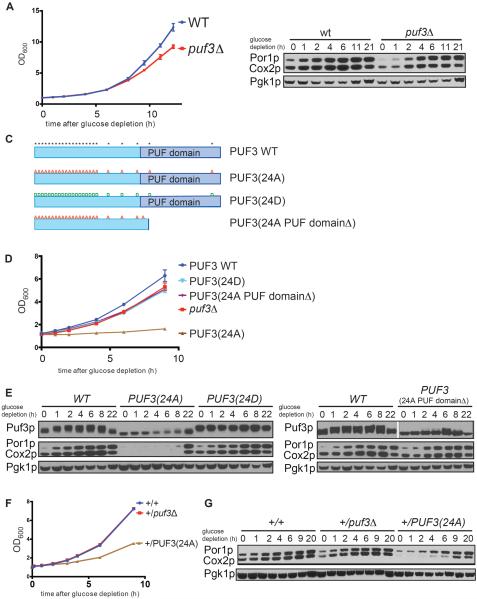
Figure 2. Puf3p phosphorylation is required for proper mitochondrial biogenesis.
(A) Growth curves of wild type and puf3Δ strains following switch to glucose depletion medium (YPGE).
(B) The abundance of mitochondrial proteins was assessed in WT and puf3Δ strains at the indicated time points following switch to glucose depletion medium (YPGE). Western blot analysis of Por1p (mitochondrial porin) and Cox2p (subunit II of cytochrome c oxidase) indicate abundance of mitochondrial proteins; Pgk1p (phosphoglycerate kinase) serves as a loading control.
(C) Schematic representation of the domain structure of Puf3p. “*” indicates identified phosphorylation sites. “A or D” denote serine or threonine residues that were mutated to alanine or aspartate. The PUF domain mediates mRNA-binding.
(D) Growth curves of WT and the indicated Puf3p mutants in glucose depletion medium.
(E) Mitochondrial biogenesis is severely compromised in the Puf3p(24A) mutant. Possible phosphorylation of Puf3p, Puf3p(24A), Puf3p(24D), and Puf3p(24A PUF domainΔ) at the indicated times following glucose depletion was assessed by Western blot using FLAG-tagged versions of these proteins. The 24A PUF domainΔ protein runs at a smaller size but the gel was cropped to show the relevant band. The accumulation of mitochondrial proteins was assessed in the same samples by Western blot. Por1p and Cox2p are mitochondrial markers, Pgk1p is loading control.
(F) The Puf3p(24A) mutant acts as a dominant negative. Growth curves of the indicated diploid strains: +/+ (WT), +/puf3Δ and +/PUF3(24A) following switch to glucose depletion medium.
(G) Mitochondrial biogenesis following glucose depletion in the indicated strains was assayed by Western blot.