Figure 3. Long-term cellular durability of reversible covalent BTK inhibitors.
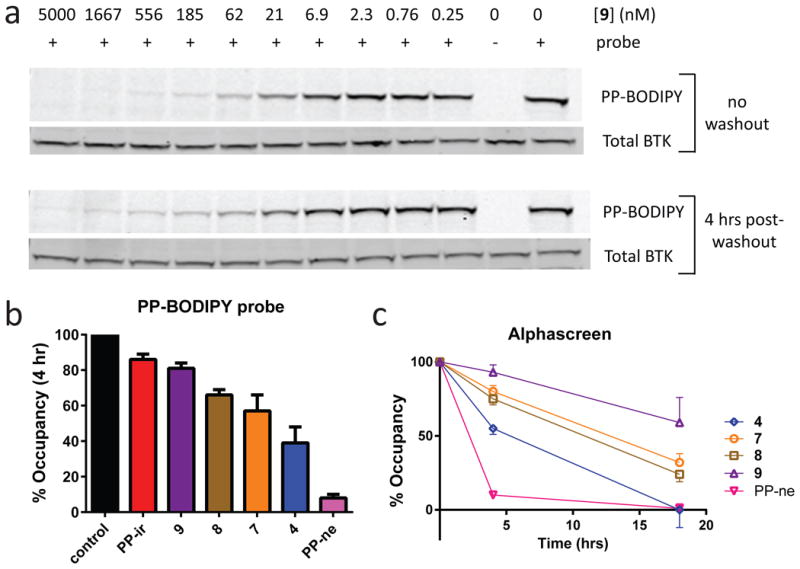
(a) Sustained BTK occupancy of compound 9 in cells 4 hrs following inhibitor washout. Ramos B cells were incubated with various concentrations of 9 and either treated with 1 μM PP-BODIPY directly (top) or washed 3 times and returned to culture for 4 hrs prior to adding 1 μM PP-BODIPY (bottom). Lysates were evaluated both for binding of the PP-BODIPY fluorescent probe to BTK (PP-BODIPY) and total BTK by Western blot (Total BTK) (n = 2). See Supplementary Fig. 25 for full gel images. (b) Reversible covalent BTK inhibitors exhibit distinct levels of durability in cells. Ramos B cells were incubated with 1 μM inhibitor, washed 3 times, and returned to culture for 4 hrs prior to addition of 1 μM PP-BODIPY. Lysates were evaluated both for binding of the PP-BODIPY probe and total BTK to calculate % Occupancy (mean ± SD, n ≥ 2) of the inhibitor (See Supplementary Fig. 14). (c) BTK occupancy of reversible covalent inhibitors 4 hrs and 18 hrs following cell washout (mean ± SD, n ≥ 2) evaluated using Alphascreen technology (Supplementary Fig. 15).
