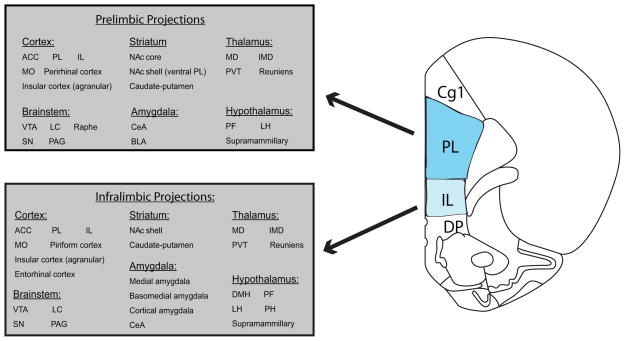
Figure 1.
Schematic summarizing the projections of PL and IL to reward-related regions. Note that although there is overlap in the targets of PL and IL fibers, in many cases the density of these projections differ greatly. For further information regarding the relative densities of PL versus IL inputs to cortical and subcortical regions, we direct the reader to several excellent papers (eg. Vertes, 2004, 2006; Heidbreder & Groenewegen, 2003). Coronal section adapted from (Paxinos and Watson, 1997) ACC, anterior cingulate cortex; BLA, basolateral amygdala; CeA, central amygdala; IL, infralimbic cortex; IMD, intermediodorsal thalamus; LC, locus coeruleus; LH; lateral hypothalamus; MD, mediodorsal thalamus; MO, medial orbital cortex; NA, nucleus accumbens; PAG, periaqueductal gray; PF, perifornical area of the hypothalamus; PH, posterior hypothalamus; PL, prelimbic cortex; PVT, paraventricular thalamus; SN, substantia nigra; VTA, ventral tegmental area.